In the world of project management, efficiency and productivity are paramount. That’s where Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method comes into play, revolutionizing the way projects are executed. By focusing on the critical path and eliminating resource constraints, this innovative approach maximizes productivity and minimizes project duration.
With Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method, project managers can confidently navigate complex projects, optimizing the use of resources and ensuring timely completion. This method harnesses the power of streamlined processes, strategic planning, and effective resource management, making it a game-changer in the realm of project management.
Let’s discover how Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method can unlock your project’s full potential and propel you towards success.
What is Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method?
Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method is a project management approach developed by Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt, a renowned Israeli physicist and management guru. Built upon the theory of constraints, this method seeks to enhance project efficiency and reduce completion time.
While conventional project management methods often concentrate on individual tasks and their estimated durations, the Critical Chain Method takes a more holistic approach.
It prioritizes the identification and management of project bottlenecks or constraints, which can arise from resource limitations, task dependencies, or uncertainties in the project environment.
By recognizing these constraints, project managers can proactively address them and mitigate their impact on project timelines. This proactive approach is a departure from the more reactive nature of traditional methods, which often result in missed deadlines and project delays.
The Critical Chain Method introduces several key concepts to optimize project performance. One such concept is the identification of the critical chain itself, which represents the sequence of tasks that determine the project’s overall duration.
By focusing on the critical chain, project managers can allocate resources and prioritize activities more effectively, reducing unnecessary delays and speeding up project completion.
4 key principles of Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method
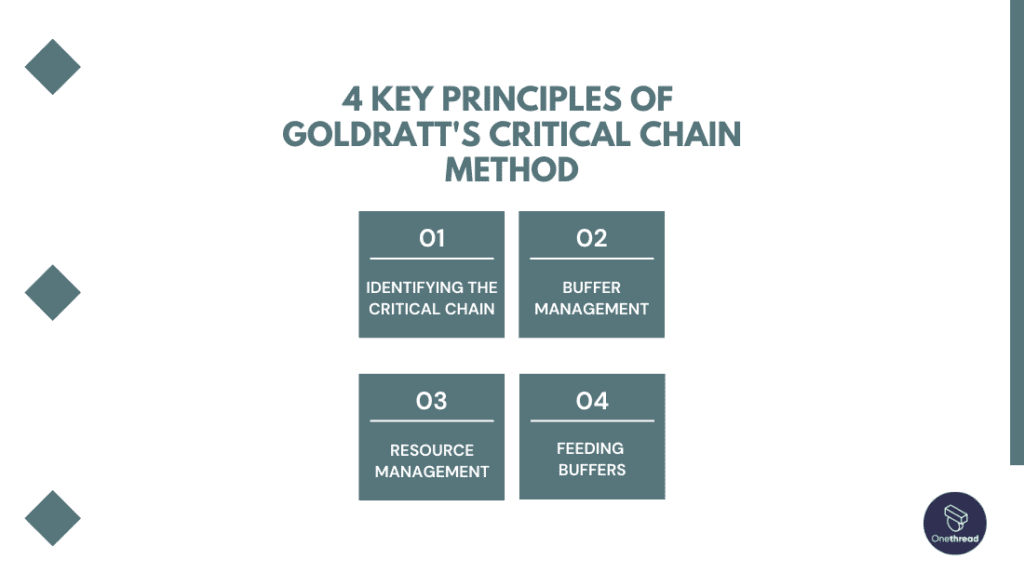
Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method is a project management approach based on four key principles: focusing on critical tasks, resource management, buffer placement, and multitasking reduction for improved project efficiency and timely delivery.
Identifying the critical chain
The critical chain refers to the sequence of tasks that determines the project’s overall duration. By identifying the critical chain, project managers can focus their efforts on optimizing these critical tasks to minimize delays.
Buffer management
In the Critical Chain Method, project buffers are introduced strategically to account for uncertainties and variations in task durations. These buffers are placed at the end of the critical chain and protect the project’s overall timeline.
Resource management
The method emphasizes the efficient allocation and utilization of resources. By eliminating resource constraints and ensuring their availability when needed, the project’s duration can be shortened.
Feeding buffers
In addition to project buffers, feeding buffers are introduced before tasks that feed into the critical chain. These buffers act as protection against potential delays in non-critical tasks, preventing them from impacting the critical chain.
Benefits of Using Critical Chain Method
With unique concept, critical chain method offers several benefits, including
- The method differs from traditional project management by prioritizing the identification and management of project bottlenecks or constraints.
- Constraints can arise from resource limitations, task dependencies, or uncertainties in the project environment.
- The critical chain refers to the sequence of tasks that determines the project’s overall duration.
- By identifying the critical chain, project managers can optimize these tasks to minimize delays and improve project timelines.
- Project buffers are strategically introduced to account for uncertainties and variations in task durations.
- These buffers are placed at the end of the critical chain and protect the project’s overall timeline.
- They act as time reserves, providing a cushion against unexpected delays and ensuring a more reliable completion date.
- Resource management is emphasized in the Critical Chain Method to ensure efficient allocation and utilization of resources.
- By eliminating resource constraints and ensuring availability when needed, project duration can be shortened.
- These buffers safeguard the critical chain, preventing disruptions and maintaining project efficiency.
- Implementing the Critical Chain Method provides greater control over project timelines and resource utilization.
What is the Critical Path?
In project management, the critical path is a principle that signifies the longest sequence of interdependent tasks, dictating the project’s most concise potential duration. It pinpoints the tasks that must be executed punctually to avert any project setbacks.
The critical path is based on task dependencies, taking into account both the duration of each task and the sequence in which they must be completed. Tasks situated on the critical path possess no slack or float, signifying that any delay in these activities will directly influence the overall duration of the project.
It helps project managers identify the most time-sensitive tasks and focus their attention on managing and tracking them closely. It provides a visual representation of the project’s longest path, offering insights into scheduling, resource allocation, and project sequencing.
Identification of critical paths help project managers determine the project’s critical milestones and ensure timely completion.
What is a Critical Chain?
The critical chain is a concept introduced by Goldratt’s Critical Chain Method, which focuses on resource constraints and buffers to improve project efficiency.
Unlike the critical path, the critical chain takes into ccount resource limitations and uncertainties when determining project duration. It identifies the sequence of tasks that are most critical in terms of resource availability and project completion.
The critical chain considers resource dependencies and prevents delays by making sure that resources are available when needed. In the critical chain, project buffers are introduced strategically to protect the overall project timeline from uncertainties and variations in task durations.
These buffers act as time reserves, placed at the end of the critical chain, providing a cushion against potential delays and safeguarding the project’s completion date.
The critical chain aims to optimize resource utilization, eliminating resource constraints to expedite project completion. Feeding buffers are also introduced before tasks that feed into the critical chain, shielding it from potential delays in non-critical tasks. The critical chain method emphasizes resource management and efficient resource allocation to maximize project efficiency.
By focusing on resource constraints and the strategic placement of buffers, the critical chain method aims to improve project duration and reduce delays caused by resource limitations.
The critical chain method enhances project planning, execution, and resource allocation by taking into account both task dependencies and resource constraints.
Key Differences between the Critical Path and the Critical Chain
Is critical path and critical chain the same? Obviously not. They have a few key differences. Let’s learn how they differ.
Focus
Critical Path
The critical path primarily focuses on the sequencing and dependencies of tasks to determine the project’s shortest duration. It identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks and highlights the must-be-completed-on-time tasks to prevent delays.
Critical Chain
On the other hand, the critical chain method places a stronger emphasis on resource constraints and aims to improve project efficiency. It considers both task dependencies and resource availability, taking into account uncertainties and variations in task durations.
Considerations
Critical Path
The critical path considers the estimated durations of individual tasks and their dependencies when determining the project’s critical path. It evaluates the sequence of tasks to identify the path that will take the longest time to complete the project.
Critical Chain
In contrast, the critical chain method takes into account not only task dependencies and durations but also resource limitations and uncertainties. It recognizes that resources can become bottlenecks in project execution and ensures that tasks are scheduled based on resource availability to prevent delays.
Resource Management
Critical Path
The critical path analysis does not explicitly address resource constraints. It focuses solely on task dependencies and durations without considering the availability or limitations of resources.
Critical Chain
In contrast, the critical chain method places significant emphasis on resource management. It seeks to maximize resource utilization and eliminate resource constraints that could impede project progress. By efficiently allocating and utilizing resources, the critical chain method aims to expedite project completion.
Buffers
Critical Path
Buffers play a crucial role in the critical chain method but are not part of the critical path analysis. In the critical chain method, project buffers and feeding buffers are strategically introduced to protect the overall project timeline.
Project buffers are time reserves placed at the end of the critical chain, accounting for uncertainties and variations in task durations. These buffers act as cushions against potential delays, safeguarding the project’s completion date.
Critical Chain
Feeding buffers, on the other hand, are placed before tasks that feed into the critical chain. They serve as protection against delays in non-critical tasks, preventing them from impacting the critical chain and overall project timeline.
Approach to Delays
Critical Path
In the critical path analysis, any delay on tasks along the critical path directly extends the project’s duration. Delays in non-critical tasks do not impact the project timeline.
Critical Chain
In contrast, the critical chain method uses buffers strategically placed in the project schedule to absorb delays and uncertainties. These buffers provide flexibility and protect the overall project timeline, ensuring that delays in non-critical tasks do not affect the critical chain.
Overall Project Optimization
Critical Path
The critical path analysis focuses on identifying the most time-sensitive tasks and critical milestones for effective project management. It helps project managers understand the tasks that require careful monitoring and attention.
Critical Chain
On the other hand, the critical chain method optimizes project efficiency by addressing both task dependencies and resource constraints. It aims to expedite project completion by considering resource availability, utilizing buffers, and managing resource dependencies effectively.
Implementation
Critical Path
The critical path analysis is widely used in various project management methodologies and software tools. It is a fundamental concept in project planning and scheduling.
Critical Chain
In contrast, the critical chain method is a specific project management approach developed by Eliyahu Goldratt. It incorporates the theory of constraints and provides a systematic framework for managing projects with a focus on resource constraints and buffers.
Parameter | Critical Path | Critical Chain |
Definition | Identifies the longest sequence of tasks that determine overall project duration and schedule. | Focuses on resource constraints and buffers to manage projects within the theory of constraints framework. |
Approach | Traditional and widely used in project management methodologies and tools. | A specific project management approach developed by Eliyahu Goldratt. |
Focus | Task dependencies and durations are the primary focus for scheduling. | Emphasizes resource management and buffer utilization to improve efficiency. |
Application | Used in various project management methodologies and software tools. | Specific to projects implementing the critical chain method. |
Resource | May not adequately account for resource limitations, potentially leading to bottlenecks. | Recognizes resource constraints and optimizes resource utilization. |
Buffer | Does not involve buffer placement; delays in non-critical tasks can affect the project schedule. | Involves strategic buffer placement to protect against uncertainties, focusing on the project’s critical chain. |
Multitasking | Multitasking is common and can lead to inefficiencies and delays. | Aims to reduce multitasking and its negative impacts on project performance. |
How to Use the Critical Chain Method in Project Management
Project managers can effectively implement the Critical Chain Method in project management. It allows for a proactive approach to mitigate uncertainties, optimize resource utilization, and safeguard the project’s overall timeline, leading to improved project efficiency and timely completion.
Identify the Critical Chain
Analyze the project’s tasks and their dependencies to determine the critical chain—the sequence of tasks that significantly impact the project’s overall duration.
Consider both task dependencies and resource constraints when identifying the critical chain.
Estimate Task Durations
Use historical data, expert judgment, and input from team members to estimate task durations.
Incorporate a degree of uncertainty and variation in task duration estimates to account for potential delays.
Determine Resource Constraints
Identify resource limitations and constraints that may affect task execution and project completion.
Assess resource availability and consider potential conflicts or bottlenecks that could impact the critical chain.
Allocate Resources Efficiently
Optimize resource allocation to ensure that critical tasks have the necessary resources available when needed.
Prioritize tasks based on resource dependencies and availability to prevent resource-related delays.
Introduce Project Buffers
Strategically introduce project buffers to protect the overall project timeline from uncertainties and variations in task durations.
Place project buffers at the end of the critical chain to provide a time reserve and absorb potential delays.
Implement Feeding Buffers
Introduce feeding buffers before tasks that feed into the critical chain.
Feeding buffers act as protective buffers against potential delays in non-critical tasks, preventing them from impacting the critical chain.
Monitor and Manage Buffers
Regularly monitor the status of the project and feed buffers throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Keep a close eye on buffer consumption and take proactive measures if buffer utilization approaches predefined thresholds.
Address Buffer Consumption
If buffer consumption exceeds predefined thresholds, investigate the underlying causes and take corrective actions.
Assess task performance, resource utilization, and potential risks to ensure that buffer consumption remains within acceptable limits.
Communicate and Collaborate
Foster open communication and collaboration among project team members.
Share buffer-related information, resource constraints, and critical chain updates to ensure a shared understanding of project priorities and goals.
Continuously Improve
Review project performance and lessons learned at the completion of each project.
Incorporate feedback and make adjustments to estimation techniques, resource allocation, and buffer management for future projects.
How Onethread Can Help a User Implement Critical Chain Method in Project Management?
Onethread can provide valuable support to users implementing the Critical Chain Method in project management by offering specific features and functionalities tailored to the method’s principles. Here’s how Onethread can help:
1. Resource Management
Onethread allows users to manage resources effectively by providing a clear overview of resource availability and allocation. Users can assign resources to tasks based on their constraints and capacities, ensuring optimal resource utilization throughout the project.
2. Buffer Placement and Management
The Critical Chain Method emphasizes the strategic placement of buffers to protect against uncertainties and variations. Onethread facilitates the creation and tracking of buffers at critical points in the project. Users can set up buffers to safeguard the critical chain and monitor their consumption to ensure project progress remains on track.
3. Task Dependency Visualization
Onethread offers visual representations of task dependencies and relationships. This feature allows users to identify the critical chain easily and focus on the tasks that significantly impact the project’s duration.
4. Real-time Updates and Collaboration
Onethread enables real-time updates and collaboration among team members. This fosters communication and coordination, allowing users to address resource constraints and potential buffer consumption issues promptly.
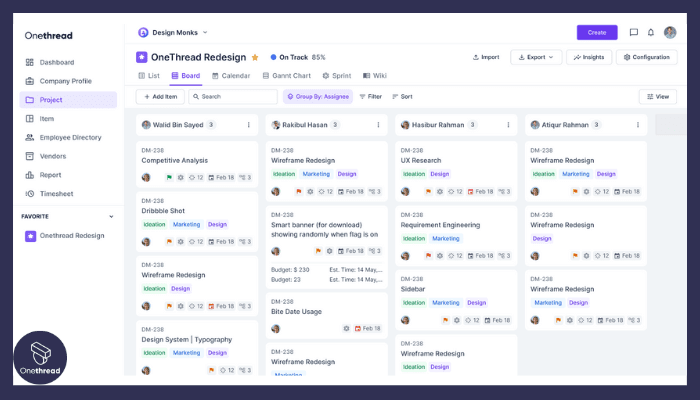
5. Buffer Feeding
The Critical Chain Method emphasizes prioritizing tasks along the critical chain to feed buffers efficiently. Onethread can help users identify tasks that contribute to buffer consumption and organize them accordingly in the project plan.
6. Task Prioritization
Users can use Onethread to prioritize tasks based on their impact on the critical chain and overall project duration. This ensures that team members focus their efforts on critical tasks and helps avoid multitasking inefficiencies.
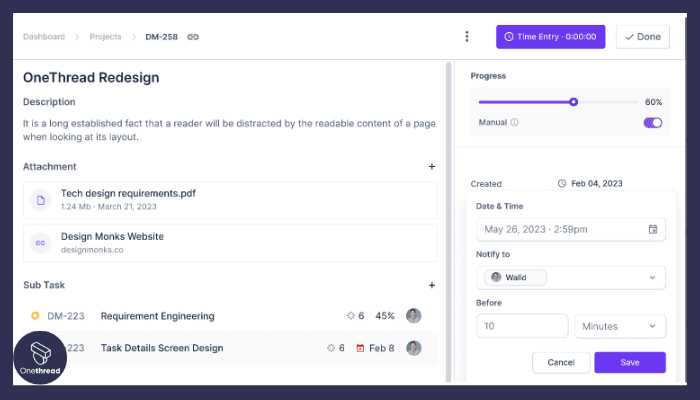
7. Project Monitoring and Reporting
Onethread offers project monitoring and reporting tools that allow users to track progress and performance against the critical chain. This provides valuable insights into the project’s status and helps users make data-driven decisions to keep the project on schedule.
8. Risk Management
Onethread’s collaborative environment enables users to identify and address potential risks proactively. By engaging team members in discussions and brainstorming sessions, users can develop contingency plans to mitigate risks and uncertainties.
9. Task Duration Estimation
Onethread can facilitate the process of estimating task durations by providing historical data and insights from previous projects. This assists in setting realistic timelines and buffers for tasks on the critical chain.
Conclusion
The Critical Chain Method offers a powerful approach to project management, focusing on resource constraints, buffer management, and efficient utilization of resources.
By identifying the critical chain, project managers can prioritize tasks and optimize their efforts to minimize delays and improve project efficiency. The strategic placement of buffers, both project buffers and feeding buffers, provides protection against uncertainties and variations in task durations, safeguarding the project’s overall timeline.
Resource management plays a crucial role, ensuring that resources are allocated and utilized effectively to prevent bottlenecks and expedite project completion.