Welcome to the world of project management, where meticulous planning and accurate predictions play a pivotal role in ensuring successful outcomes. Among the many critical aspects of project planning, cost estimation in project management stands tall as a fundamental pillar.
As a project manager, you know that cost estimation lays the groundwork for budgeting, resource allocation, and overall project feasibility. A well-crafted cost estimation process provides invaluable insights into the financial requirements, potential risks, and project scope.
In this article, we will delve into the art and science of cost estimation in project management, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to navigate this essential process with confidence and precision.
What Is Cost Estimation in Project Management?
Cost estimation in project management refers to the systematic process of predicting and calculating the financial resources required to complete a specific project.
It involves assessing various cost components, such as labor, materials, equipment, overhead, and other expenses, to create a comprehensive budget that outlines the financial scope of the project.
A well-executed cost estimation is vital for project planning and decision-making. It helps project managers and stakeholders determine the project’s feasibility, allocate resources effectively, and set realistic expectations for project outcomes.
By providing insights into the financial aspects of the project, budget estimation enables better risk assessment and allows proactive measures to be taken to avoid budget overruns and potential financial setbacks.
Cost estimation is not a one-time event; it is an ongoing process that starts during the project’s initiation and continues throughout its lifecycle.
As the project progresses and more information becomes available, cost estimates may be revised and refined to reflect changes in scope, resource availability, or external factors that could impact the project’s financial landscape.
In essence, cost estimation in project management is a fundamental tool that empowers project managers to plan and execute projects with efficiency, control expenses, and ultimately deliver successful outcomes within the allocated budget and resources.
Why Is Cost Estimation Important in Project Management? – Benefits of Estimating Project Cost
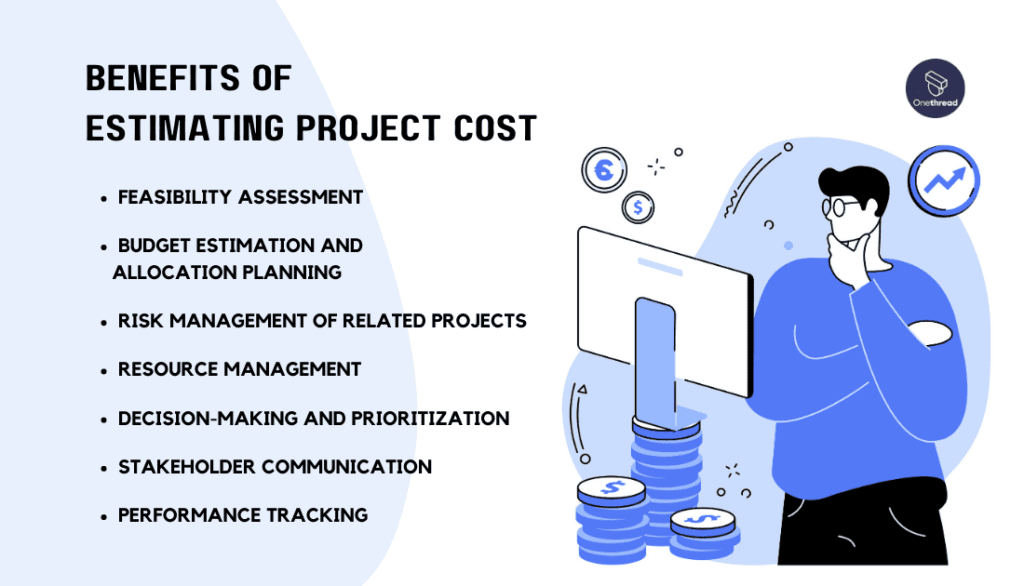
Project cost estimating holds paramount importance due to its profound impact on the success and viability of a project. As a project manager, you must recognize the significance of effective cost estimation, and here are the key reasons why it is so crucial:
Budget Estimation and Allocation Planning
Project cost management serves as the foundation for budget planning. By accurately predicting the financial requirements of a project, you can allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that you have sufficient funds for each phase and task.
A well-planned budget prevents overspending, avoids financial bottlenecks, and maintains financial stability throughout the project’s lifecycle. You can also utilize features like custom fields to track your budget.
Feasibility Assessment
Rigorous cost estimation allows you to assess the feasibility of a project before committing resources. By understanding the financial implications, you can determine if the project aligns with the organization’s financial capabilities and strategic goals.
If the estimated costs exceed the benefits or available funds, it may signal the need for reevaluation or reassessment of the project’s scope.
Risk Management of Related Projects
Accurate cost estimation enables better risk management. By identifying potential cost overruns or underestimations early on, you can devise risk mitigation strategies to safeguard the project’s financial health.
Understanding the financial risks empowers you to make informed decisions and adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
Resource Management
With proper cost estimation, you can allocate resources optimally while ensuring revenue recognition aligns with financial reporting standards, helping track income accurately throughout the project lifecycle.
Whether it’s human resources, materials, or equipment, knowing the financial demands of each aspect enables you to strike a balance between availability and necessity. This leads to improved resource utilization and better time management and it minimizes wastage.
Decision-making and Prioritization
Cost estimation facilitates data-driven decision-making. As you have a clear understanding of the financial implications of various project options, you can prioritize tasks and allocate resources to areas that offer the highest value and impact on project objectives.
Stakeholder Communication
Transparent and accurate cost estimation enhances communication with stakeholders. When stakeholders are aware of the financial aspects of the project, they can make informed decisions and offer support based on realistic expectations.
Performance Tracking
Cost estimation provides a baseline for performance tracking. By comparing actual costs with estimated costs, you can evaluate the project’s financial progress and identify areas that require adjustments or corrective actions. With an efficient project management tool, you don’t need any spreadsheet or any similar tools that’s typically less efficient.
What Are the Elements of Cost Estimation in Project Management? – Efficient Cost Breakdown
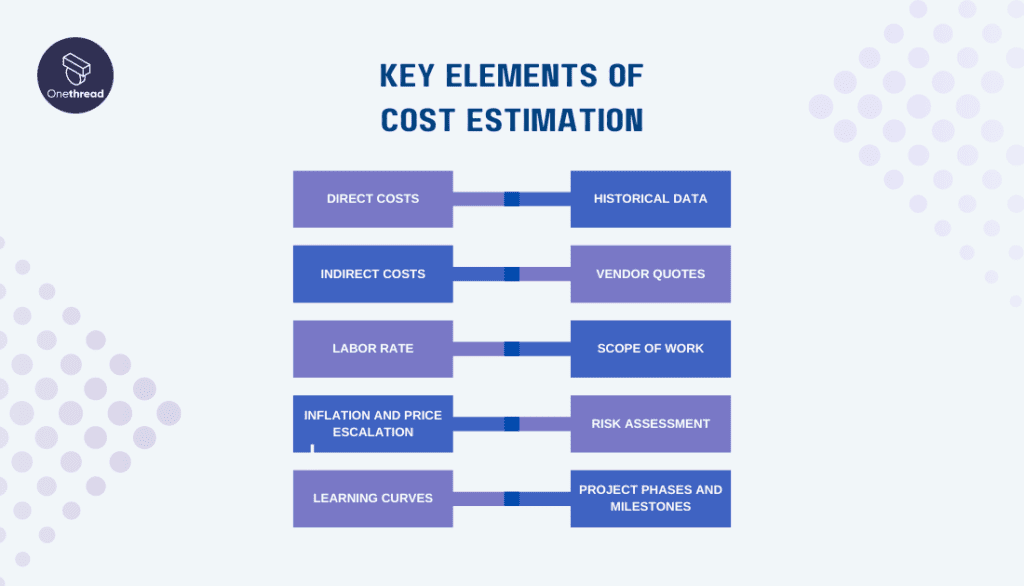
Cost estimation in project management involves considering various elements to create a comprehensive and accurate estimate. These elements collectively contribute to determining the total cost of the project. Here are the key elements of cost estimation:
Direct Costs
Direct costs are expenses that can be directly attributed to a specific project activity or work package. They typically include labor costs (wages and benefits of project team members), material costs (raw materials or purchased components), and equipment costs (rental or depreciation of machinery and tools) that are directly involved in executing the project tasks.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, are expenses that cannot be directly attributed to a particular project task but are necessary to support the overall project. These costs encompass items like general administration, utilities, office space, and other shared resources that are essential for project operations.
Contingency Reserves Contingency reserves are a provision for unexpected events and risks that might impact the project’s cost. It is crucial to include a buffer in the cost estimate to address unforeseen situations and potential cost overruns.
Labor Rate
Labor rate refers to the hourly or daily cost of labor for each resource involved in the project. It takes into account the salaries, benefits, and any additional labor-related expenses.
Inflation and Price Escalation
Cost estimation must account for inflation and potential price escalation of materials or resources over the project’s duration. Prices may fluctuate, and failure to consider this can lead to inaccurate cost projections.
Learning Curves
Learning curves represent the principle that as workers become more experienced and efficient with a repetitive task, the time and cost required for each subsequent unit decreases. This element is especially relevant for projects involving repetitive activities.
Historical Data
Historical cost data from similar past projects can be a valuable reference for estimating costs. Past project performance and expenses provide insights into how certain elements impact costs and aid in making more reliable estimates.
Vendor Quotes
For certain resources or services to be outsourced or procured from external vendors, obtaining quotes or bids from suppliers provides accurate cost data.
Scope of Work
The project’s scope defines what needs to be accomplished. A well-defined scope ensures that all relevant cost elements are accounted for in the estimation process.
Risk Assessment
Evaluating potential risks and their financial impact is essential in cost estimation. This includes identifying both threats and opportunities that could affect project costs.
Project Phases and Milestones
Breaking the project into distinct phases and milestones helps in estimating costs for each stage separately, making the overall estimation process more manageable and accurate.
5 Methods of Project Cost Estimation – Easy Project Cost Management for Project Managers
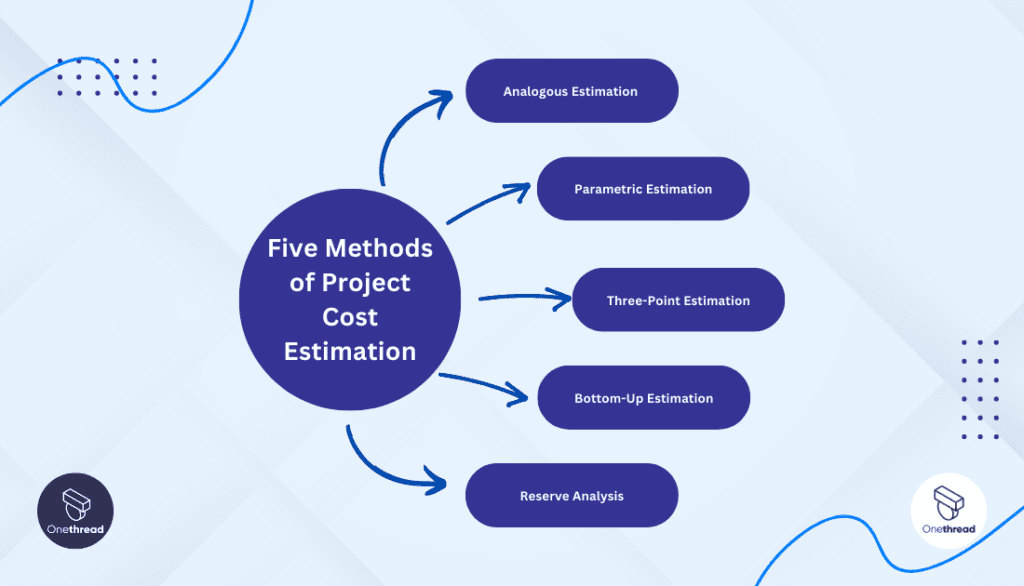
Project cost estimation involves employing various methods to predict and calculate the financial requirements of a project. These methods vary in complexity and accuracy. Here are the five commonly used methods of project cost estimation:
Analogous Estimation (Top-Down Estimating of Projects)
This method relies on previous data from similar past projects as a reference to estimate the costs of the current project. Project managers use their experience and judgment to identify similarities between the current project and previous ones to make a rough estimation of cost.
While it is a quick and simple method, its accuracy heavily depends on the similarity of the projects used for comparison.
Parametric Estimation
Parametric estimation entails utilizing statistical correlations within historical data and specific project parameters to estimate costs. For example, if there is a consistent relationship between project size (measured in lines of code) and development effort, this relationship can be used to estimate the effort for a new project based on its size.
Parametric estimation can be more accurate than analogous estimation, but it requires a reliable database of historical data and well-defined parameters.
Three-Point Estimation (PERT – Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
The three-point estimation is a probabilistic method that takes into account uncertainty in cost estimates. Project managers provide three estimates for each activity or task: the optimistic (O), most likely (M), and pessimistic (P) costs.
Using these values, a weighted average is calculated to arrive at the expected cost. The formula for the expected cost (C) is (O + 4M + P) / 6. This method provides a more realistic and risk-aware cost estimate.
Bottom-Up Estimation
Bottom-up estimation involves breaking down the project into individual work packages or tasks and estimating the cost of each element. The costs of all work packages are then aggregated to derive the total project cost.
This method offers a detailed and accurate estimation, as it accounts for the unique characteristics of each task. However, it can be time-consuming and is best suited for well-defined projects.
Reserve Analysis
Here, you keep the contingency reserves aside and address all the uncertainties and risks impacting the project’s cost. Project managers use risk assessments and historical data to determine an appropriate contingency reserve to be added to the estimated cost.
The reserve analysis helps to account for unforeseen events and ensures that the project remains within budget even if unexpected situations arise.
How to Estimate Project Costs As a Project Manager: 10 Steps to Estimate Costs Effectively

Estimating project costs is a critical process that requires careful analysis and consideration. Follow these step-by-step guidelines to effectively estimate project costs:
Define Project Scope
Clearly define the project scope, outlining all the deliverables, tasks, and objectives. A well-defined scope provides the foundation for accurate cost estimation.
Identify Cost Elements
Break down the project into its components, identifying all the direct and indirect cost elements. This includes labor, materials, equipment, overhead, contingency reserves, and any other relevant expenses.
Gather Historical Data
Use historical data from past similar projects to gain insights into cost patterns and performance metrics. This data serves as a valuable reference point for estimation.
Choose Estimation Methods
Select appropriate estimation methods based on the project’s nature and available data. Consider using techniques like analogous estimation, parametric estimation, three-point estimation, or bottom-up estimation.
Calculate Task Costs
For bottom-up estimation, calculate the costs of individual tasks or work packages. Include labor hours, material costs, and any other direct expenses associated with each task.
Incorporate Contingency Reserves
Account for uncertainties and risks by adding contingency reserves to the estimated costs. The amount of reserves should be based on the project’s risk assessment and tolerance.
Summarize and Validate
Summarize all cost estimates and validate them with stakeholders, team members, and subject matter experts. Incorporate their feedback and ensure that the estimates align with the project’s goals and requirements.
Document Assumptions
Clearly document all assumptions made during the estimation process. This transparency helps in future decision-making and adjustments if needed.
Update Throughout the Project
Cost estimation is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor and update the estimates as the project progresses and new information becomes available.
Review and Refine the Cost Estimates
Review the cost estimates regularly during project execution to ensure accuracy. If necessary, refine the estimates based on actual performance and lessons learned from completed tasks.
How Onethread Enhances Cost Estimation?
In today’s complex business landscape, leveraging advanced tools like Onethread can significantly enhance the effectiveness of cost estimation processes. Let’s explore how Onethread’s features can help streamline and improve cost estimation for a wide range of projects.
Data-Driven Insights
Onethread incorporates historical project data and industry benchmarks to provide data-driven insights into cost estimation. By analyzing past project costs, team performance, and resource utilization, the platform helps teams make informed decisions about future project budgets.
Resource Allocation Optimization
Onethread’s resource management tools enable teams to allocate resources efficiently, minimizing overallocation and reducing costs associated with underutilized resources. This feature ensures that project resources are utilized optimally, leading to more accurate cost estimates.
Cost Tracking and Monitoring
Onethread allows project managers to track and monitor costs throughout the project lifecycle. By integrating with financial systems, the platform provides real-time insights into actual expenses versus estimated costs, facilitating adjustments and better financial control.
Risk Assessment and Contingency Planning
Estimating costs involves accounting for potential risks and uncertainties. Onethread’s risk assessment tools help teams identify potential cost-related risks and create contingency plans, enhancing the accuracy of cost estimates and reducing the likelihood of budget overruns.
Final Thoughts
To summarize, mastering the art of cost estimation in project management is indispensable for any successful project. By adopting robust estimation techniques, continuously monitoring and adjusting the budget, and accounting for potential risks, you can enhance your project’s chances of reaching its objectives on time and within the allocated resources.
Remember, cost estimation is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that evolves with the project. Embrace the challenges and opportunities it presents, and always be open to refining your estimates based on new information.
Armed with this understanding, you can confidently lead your team and stakeholders towards project success while keeping financial constraints well-managed. May your future projects be marked by efficiency, accuracy, and prosperity. Happy cost estimating!
