The need for efficient and flexible systems has become paramount in today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where connectivity is constant and communication spans across time zones. Enter the world of asynchronous communication, a concept revolutionizing how we interact and collaborate.
Asynchronous communication embraces the power of independence and freedom, allowing individuals to exchange information and ideas without being confined by real-time constraints. By breaking free from the traditional limitations of synchronous communication, asynchrony enables productivity, creativity, and collaboration on a global scale.
This article will delve into the intricacies of asynchronous communication and explore its remarkable benefits in fostering seamless connections and empowering individuals to work at their own pace.
What is Asynchronous Communication?
Asynchronous communication refers to a method of exchanging information and messages without the need for immediate or real-time interaction.
Unlike synchronous communication, which relies on instant responses, asynchrony allows individuals to communicate and collaborate at their own convenience.
This type of communication is particularly beneficial for teams and individuals who operate in different time zones or have conflicting schedules.
It provides the flexibility to participate in discussions, share updates, and provide feedback without the constraints of simultaneous availability.
Asynchronous communication fosters productivity by reducing interruptions and enabling deep focus on tasks. It also promotes inclusivity by accommodating diverse working styles and allowing individuals to contribute regardless of their location or time constraints.
What are a few Examples of Asynchronous Communication?
The concept of asynchronous communication becomes clear when considering the following scenario:
Alexis and David are part of a 10-person team that holds a daily 15-minute round-up session to discuss progress, recent developments, and the agenda. Whether held in the conference room or on Zoom for remote workdays, this meeting represents synchronous communication.
Here are three examples illustrating asynchronous communication:
Example 1: After the meeting, a team member voluntarily writes up meeting minutes and shares them via email. This dissemination of information allows team members to catch up on missed details at their convenience.
Example 2: Alexis is occupied with tasks A, B, and C, while David requires clarification on task D. Instead of interrupting Alexis, David reaches out through instant messaging, knowing she might be focused on other tasks. He communicates his query without demanding immediate time or attention. Alexis addresses the query later when she completes her tasks.
Example 3: Asynchronous communication is also evident in email exchanges. For instance, when receiving a proposal that requires an immediate decision, you can respond at your convenience rather than feeling compelled to provide an immediate yes or no.
What are the Benefits of Asynchronous Communication?
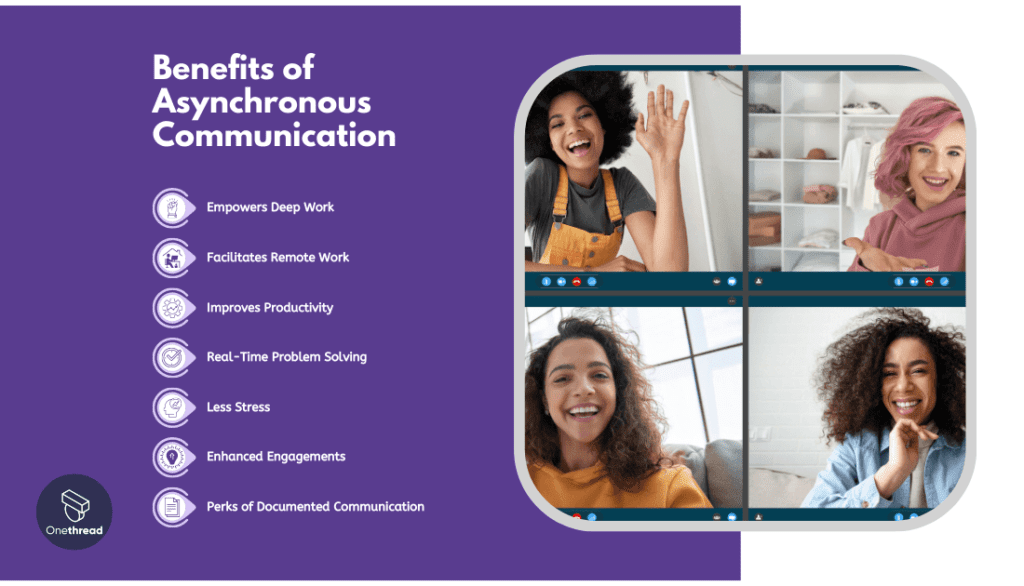
In today’s professional world, asynchronous communication has become increasingly prevalent. It is favored by virtual, office-bound, and hybrid teams for its numerous advantages. Here’s why:
#1 Empowers Deep Work
Deep work refers to immersing oneself in tasks with intense focus and minimal distractions. Asynchronous communication is ideal for deep work because it eliminates interruptions caused by synchronous communication methods like unexpected calls and instant messages. This allows individuals to give undivided attention to their tasks.
#2 Facilitates Remote Work
Asynchronous communication is particularly beneficial for remote teams operating across different time zones. With no immediate response expectations, it facilitates remote work by providing flexibility and convenience. It supports collaboration, idea sharing, and effective teamwork regardless of geographical barriers.
#3 Improves Productivity
Asynchronous communication minimizes distractions, enabling individuals to allocate specific time for message correspondence and issue resolution. This dedicated focus leads to enhanced productivity. Additionally, it facilitates more efficient planning processes as teams are not reliant on immediate answers and quick feedback.
#4 Real-Time Problem Solving
Synchronous communication eliminates the need for waiting to resolve issues. Unlike asynchronous communication, where projects can often stall while waiting for responses, synchronous communication ensures that problems are addressed promptly. This advantage maximizes production time and minimizes delays.
#5 Less Stress
One of the key advantages of asynchronous communication is its ability to reduce stress. Immediate response expectations can create an overwhelming burden, leading to workplace stress and anxiety. Asynchronous communication relieves this stress by allowing individuals to respond independently, fostering clear-headedness and stress-free communication.
#6 Enhanced Engagements
Synchronous communication opens up avenues for more profound interactions within your team. Engaging in activities like brainstorming and collectively solving complex problems becomes more fruitful as it allows for real-time conversations, nonverbal cues, and immediate feedback.
#7 Perks of Documented Communication
Asynchronous communication enables the documentation of conversations, shared ideas, and important information. It promotes transparency and ensures timely dissemination of updates. It also helps create a detailed record or wiki for the entire team or organization, making information easily accessible and secure.
Drawbacks of Synchronous Communication
While synchronous communication offers several advantages, it also presents a few drawbacks to consider.
Disruption of Focus
Despite the apparent convenience of real-time conversations, they can significantly disrupt your focus. Interruptions such as colleagues stopping by your desk or receiving instant messages on platforms like Slack for immediate responses can hinder the task. As a result, your attention may be divided, affecting both the ongoing conversation and your current work.
Challenges for Individuals in Different Timezones
Synchronous communication can pose difficulties for teams spanning various time zones, leading to imbalances in work-life harmony and potential burnout. The optimal communication time for one team member may coincide with the middle of the night for another.
Synchronous communication requires participants to be available and online simultaneously. This can be challenging, especially in global teams with different time zones, leading to scheduling conflicts and difficulties in finding a suitable meeting time for everyone.
If synchronous communication becomes the norm, its effectiveness can be compromised.
Bandwidth and Technical Issues
Synchronous communication relies on stable internet connections and suitable technology. Bandwidth constraints or technical glitches can disrupt meetings, causing frustration and hindering effective communication.
Limited Participation Opportunities
In synchronous communication settings, only individuals present at the scheduled time can actively participate. This may exclude team members who are unavailable due to other commitments or time zone differences.
Inefficient for Certain Tasks
Some tasks, such as individual work, decision-making that requires research, or complex problem-solving, might be better suited for asynchronous communication to allow for more thoughtful and in-depth contributions.
Increased Potential for Interruptions
During synchronous communication, participants may experience interruptions from other colleagues or external factors, disrupting the flow of communication.
Despite these drawbacks, synchronous communication remains a valuable tool for real-time collaboration, team-building, and addressing urgent matters. The key is to strike a balance between synchronous and asynchronous communication methods, leveraging each approach’s strengths to optimize overall communication effectiveness and efficiency.
Why Asynchronous Communication Falls Short?
Even though asynchronous communication offers numerous advantages, there are instances where it may not be suitable or beneficial. Here are five reasons why asynchronous communication may not work effectively:
Lack of Clarity in Expression
For effective asynchronous communication, the sender and recipient must provide clear and detailed messages. Coherent and comprehensive communication is essential to ensure a meaningful response. Since asynchronous communication leaves a trail, maintaining accurate, candid, coherent, and concise records becomes even more crucial.
Absence of Defined Response Time
Without a defined response time, the sender is uncertain when to expect a reply, while the recipient may feel pressured to respond promptly. This ambiguity can lead to confusion and frustration. Setting a reasonable response time is necessary to facilitate meaningful and timely follow-ups.
Insufficient Provision of Resources
When utilizing asynchronous communication, the sender expects a straightforward and comprehensive response. However, if the recipient fails to provide sufficient details or relevant resources, the communication may fail to achieve its intended purpose.
Guiding team members with clear instructions and providing necessary links, files, documents, and other resources can enhance the effectiveness of asynchronous communication.
Partial Withholding of Information
Transparency is crucial for effective collaboration, which includes the flow of information and resources in an asynchronous communication setup. Recipients should feel empowered to share doubts or uncertainties and seek additional guidance from their superiors when needed.
Reduced Sense of Connection
Asynchronous communication lacks the personal touch of face-to-face or real-time interactions. It can lead to a sense of disconnect among team members, making it harder to build strong relationships and camaraderie.
Inefficient Problem Resolution
Some issues require quick resolution and immediate attention. In asynchronous communication, urgent matters may not receive prompt responses, leading to delays in resolving critical problems.
Potential Miscommunication
In written communication, nuances of tone and emotion can be lost, leading to miscommunication or unintended offense. This is particularly true in text-based mediums like emails or messages.
Besides, delicate or emotionally charged topics are often better discussed in real-time, where immediate feedback and empathy can be provided. Asynchronous communication might not be as effective in handling such situations.
Overwhelming Workloads, Hindered Creativity and Collaboration
In an asynchronous communication culture, individuals might feel the need to constantly check messages and respond promptly, leading to increased stress and difficulty in achieving work-life balance.
On the other hand, brainstorming and creative problem-solving can thrive in real-time discussions where ideas can flow freely. Asynchronous communication might limit spontaneous collaboration and hinder creativity.
Less Engaging Meetings
Virtual meetings conducted asynchronously through recorded videos or documents may lack the interactive and engaging nature of live discussions, leading to decreased attention and participation.
Missed Opportunities for Building Rapport
In-person interactions and real-time discussions foster stronger relationships and trust among team members. Asynchronous communication might miss the chance to build rapport, especially in remote or distributed teams.
Establishing a solid chain of command and fostering workplace transparency can enhance the success of asynchronous communication.
Confusion between Asynchronous and Synchronous Communication
Setting time limits for response in asynchronous communication can inadvertently create an expectation of immediate replies, blurring the line between asynchronous and synchronous communication.
To address this issue, it is important to monitor the minimum response time of team members to asynchronous messages. Defining different communication channels for each type of communication can help avoid misconceptions and ensure effective communication practices.
Methods for Asynchronous Communications
Asynchronous communication has become an integral part of modern work environments, enabling efficient collaboration and information exchange across diverse teams and time zones. Several methods and tools facilitate seamless asynchronous communication, each catering to specific needs and preferences.
Email: One widely used method is email, a versatile tool that allows individuals to convey detailed information, share files, and maintain threaded conversations. Its asynchronous nature ensures recipients can respond at their convenience, without the pressure of immediate interaction. However, email threads can become unwieldy for complex discussions.
Instant Messaging Platforms: Another valuable method is instant messaging platforms, such as Slack and Microsoft Teams. These tools offer real-time chat functionality and organized channels, enhancing team communication while allowing individuals to catch up on messages they missed. Their asynchronous nature allows participants to respond when they are available, promoting a balance between work and focus.
Document Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools like Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365 facilitate asynchronous teamwork on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations. Team members can contribute at different times, view revisions, and provide feedback without the need for simultaneous engagement.
Project Management Tools: Project management platforms, including Trello and Asana, enable teams to collaborate asynchronously on tasks, set deadlines, and track progress. This method enhances accountability and ensures that project-related discussions are accessible to all team members.
Blogs and Forums: Blogs and discussion boards are effective for sharing information, insights, and updates. Team members can contribute at their own pace, fostering knowledge sharing and thoughtful discourse.
What are top Tools for Asynchronous and Synchronous Communication?
Discover the essential tools for asynchronous communication, enabling efficient collaboration. These tools are vital for seamless interaction, enhancing productivity, and fostering effective team collaboration regardless of physical distance.
1. Onethread
Onethread is a software development approach that executes tasks sequentially in a single thread rather than utilizing multiple threads or parallel processing. It simplifies code execution and reduces complexity but may limit performance in certain scenarios that could benefit from parallelism.
How Onethread Acts As An Asynchronous Communication Tool
Task Management for Autonomy and Flexibility
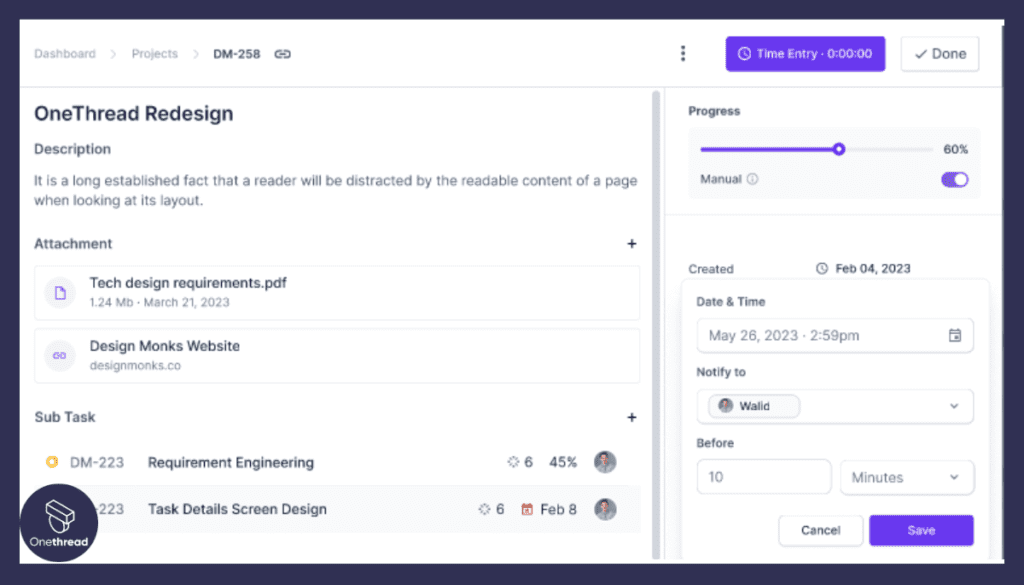
Onethread’s task management feature empowers team members to organize and prioritize tasks independently. Each member can access their tasks, set deadlines, and make progress at their own pace. This flexibility not only encourages autonomy but also accommodates different working styles, enabling individuals to contribute their best work when it suits them.
Real-time Messaging for Fluid Discussions
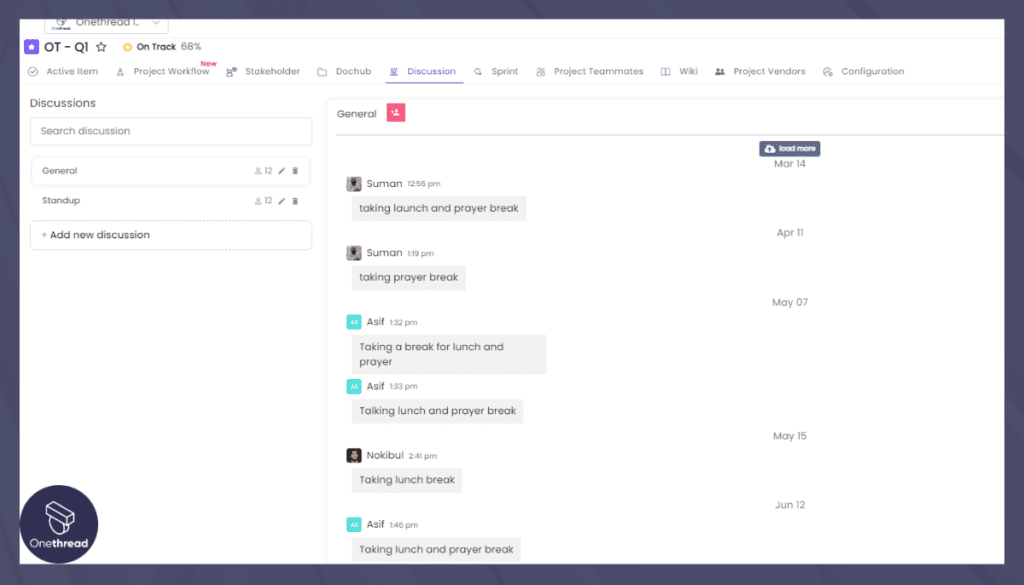
While asynchronous, Onethread’s real-time messaging feature bridges the gap between team members spread across various time zones. Engage in fluid discussions, ask questions, and offer insights, knowing that responses will be there when your colleagues log in. This fosters meaningful exchanges without the pressure of immediate replies, nurturing thoughtful and well-considered conversations.
Collaborative Document Sharing and Editing
Onethread revolutionizes document collaboration through its seamless file sharing and editing capabilities. Team members can access shared documents, make revisions, and leave comments asynchronously. This ensures that the evolution of project documents is continuous, and every contributor’s input is acknowledged, regardless of their availability.
Notifications and Reminders for Time Management
In an asynchronous setting, managing time effectively is crucial. Onethread’s customizable notifications and reminders ensure that deadlines and updates are communicated to all team members. Whether it’s a pending task or an important milestone, these notifications keep everyone informed, helping to maintain a sense of accountability and ensuring timely progress.
Data Visualization for Insights Across Time Zones
Onethread’s data visualization tools offer a unique advantage for asynchronous collaboration. Team members, regardless of their geographic location, can analyze project progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Visual representations of data transcend time barriers, ensuring that everyone remains aligned with project goals and informed about the project’s trajectory.
Asynchronous communication thrives within Onethread’s ecosystem, where task management, real-time messaging, collaborative document editing, notifications, and data visualization harmonize to create a seamless workflow across diverse schedules. With Onethread, your team reaps the benefits of flexibility, effective collaboration, and enhanced productivity, proving that synchronous interaction is not the sole driver of success in the modern work landscape.
Pricing:

- Free Forever: Starter for free with limited features
- Growth Plan: 200 BDT/user/month
- Scale Plan: 400 BDT/user/month
- Enterprise Plan: Contact Onethread for Quotation
2. Google Drive
Google Drive is a cloud-based storage and collaboration platform that allows users to create, edit, and share documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and more. It offers real-time collaboration, version control, and seamless integration with other Google Workspace tools.
Key Features:
- Document creation and editing
- File storage and sharing
- Real-time collaboration
Pricing:
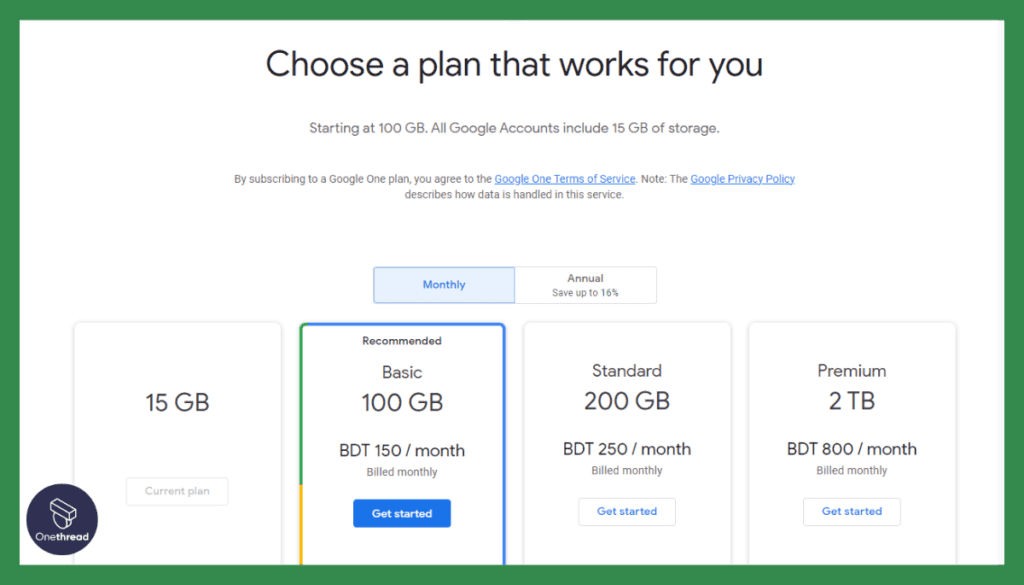
- Free: 15 GB of storage
- Paid plans start at $1.99/month for 100 GB
3. Loom
Description: Loom is a video messaging and recording tool that allows users to capture their screens, record videos, and share them instantly. It simplifies asynchronous communication by providing a visual and interactive way to convey information, collaborate, and provide feedback.
Key Features:
- Screen and video recording
- Instant sharing and commenting
- Video messaging and communication
Pricing:
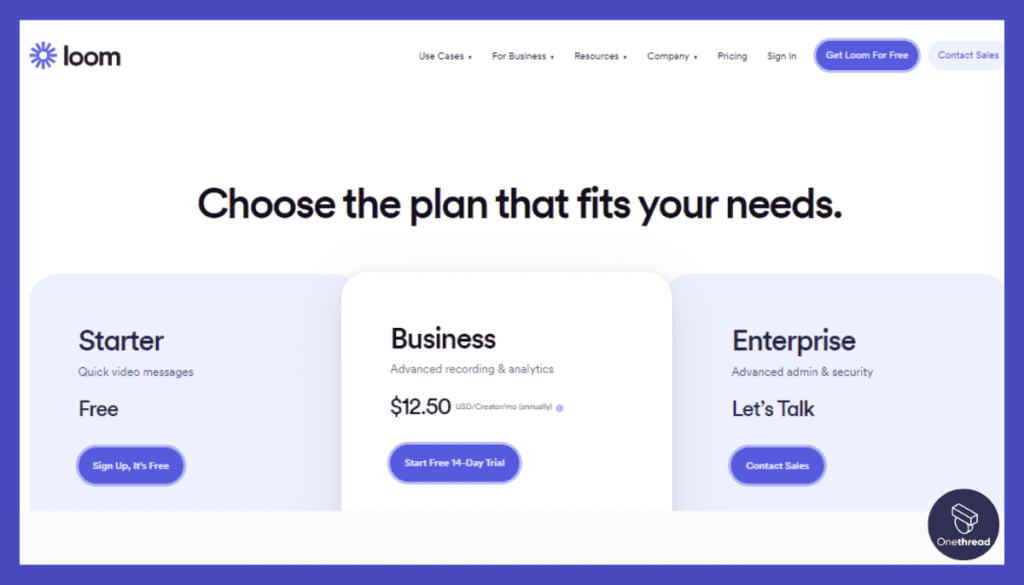
- Free: Limited features and storage
- Paid plans start at $8/month per user.
4. Slab
Slab is a knowledge management and collaboration tool designed to help teams create, organize, and share documentation. It enables asynchronous communication by providing a centralized platform for storing and accessing important information, facilitating collaboration, and ensuring knowledge retention.
Key Features:
- Knowledge management and documentation
- Team collaboration and sharing
- Version control and search functionality
Pricing:
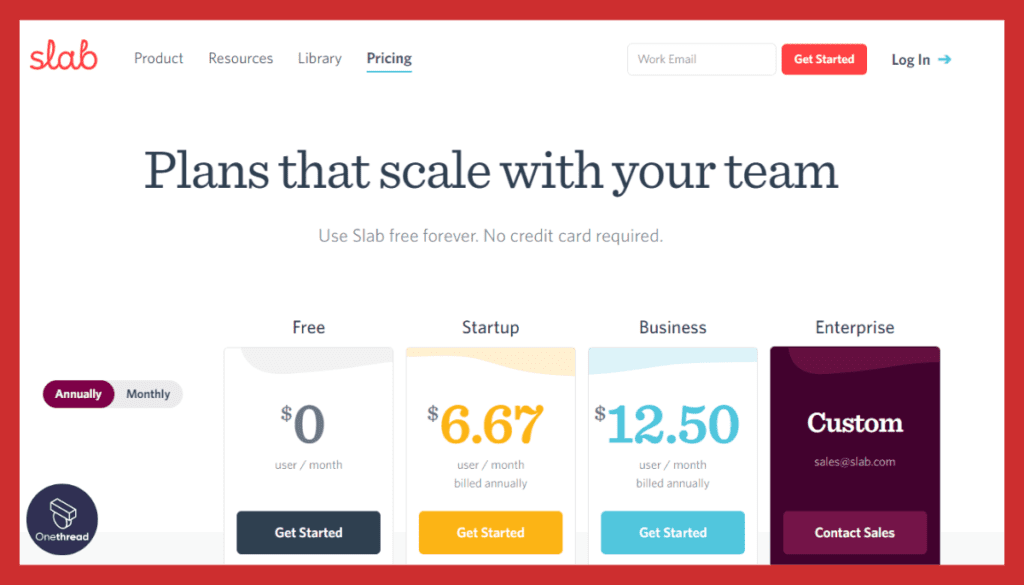
- Free: Limited features and storage
- Paid plans start at $6/user/month.
5. Tettra
Tettra is a knowledge management tool that allows teams to create and share internal documentation. It promotes asynchronous communication by providing a centralized repository for important information, ensuring easy access, and enabling collaboration. It integrates with popular tools like Slack, Google Drive, and Trello.
Key Features:
- Internal knowledge base
- Team documentation and collaboration
- Integration with popular tools
Pricing:
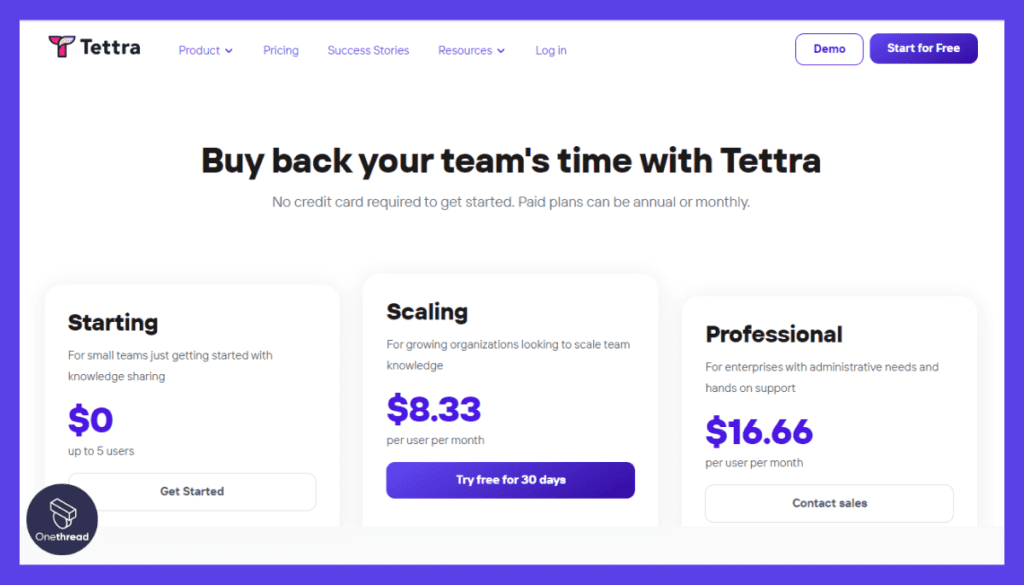
- Free trial available
- Paid plans start at $5/user/month.
6. Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams is a collaboration platform that combines chat, video meetings, and file sharing. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for team communication, allowing users to work together efficiently and seamlessly.
Key Features:
- Chat-based collaboration and file sharing
- Video and audio conferencing capabilities
- Integration with Microsoft Office applications
Pricing:
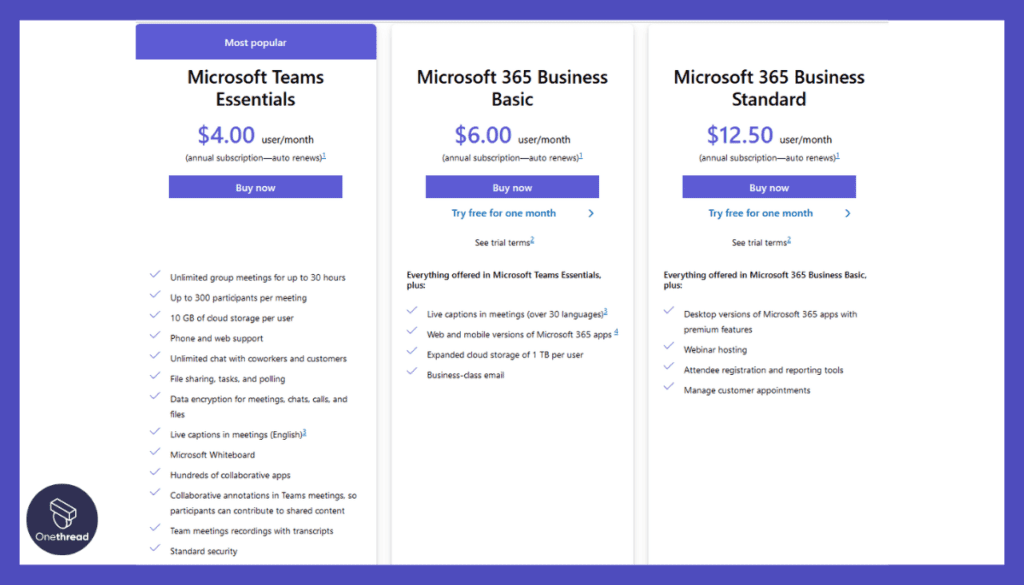
- Microsoft Teams offers a free plan with limited features. Paid plans are available as part of the Microsoft 365 suite, with pricing starting at $5 per user per month.
7. Google Chat
Google Chat is a messaging and collaboration tool that enables users to communicate in real-time. It integrates with other Google Workspace apps, allowing seamless file sharing and collaboration within the Google ecosystem.
Key Features:
- Direct messaging and group chats
- Integration with Google Workspace apps
- Powerful search and message archiving capabilities
Pricing:

- Google Chat is free as part of Google Workspace (formerly G Suite). Google Workspace plans to start at $6 per user per month.
8. Asana
Asana is a project management tool that facilitates asynchronous communication among team members. It allows for organizing tasks, discussions, and files, making it easier for teams to collaborate and track progress.
Key Features:
- Task management and assignment
- Collaboration on project-specific discussions
- File sharing and document organization
Pricing:
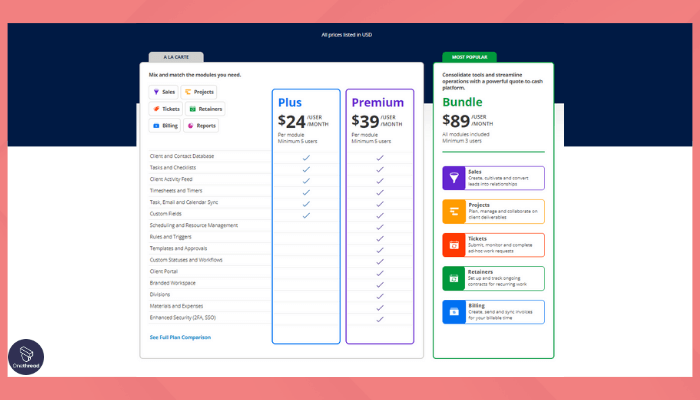
- Asana offers a free plan included basic features. Paid plans start at $10.99 per user per month.
9. Trello
Trello is a flexible management tool for projects that uses lists, cards, boards to help teams prioritize tasks and assemble. It provides a visual overview of project progress and facilitates asynchronous communication around specific tasks.
Key Features:
- Visual task boards for project management
- Assignment of tasks and due dates
- Integration with various productivity tools
Pricing:
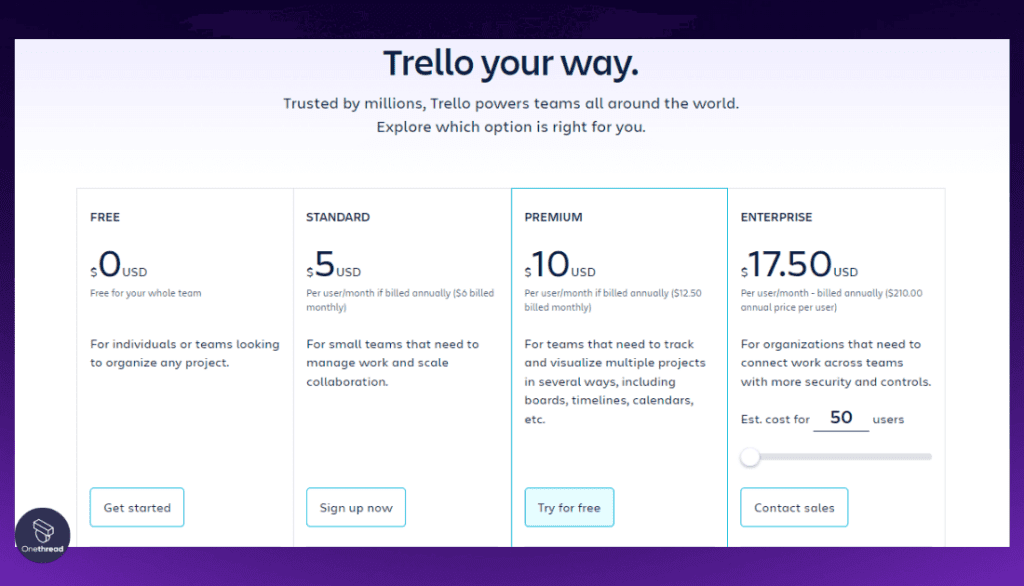
- Trello offers a free plan with basic features. Paid plans, including more advanced features, start at $12.50 per monthly user.
10. Basecamp
Basecamp is a collaboration and project management tool focusing on ease of use and clarity. It provides a central hub for team communication, allowing users to share messages, track tasks, and collaborate on documents.
Key Features:
- Message boards for team discussions
- Task tracking and assignment
- Document and file sharing
Pricing:
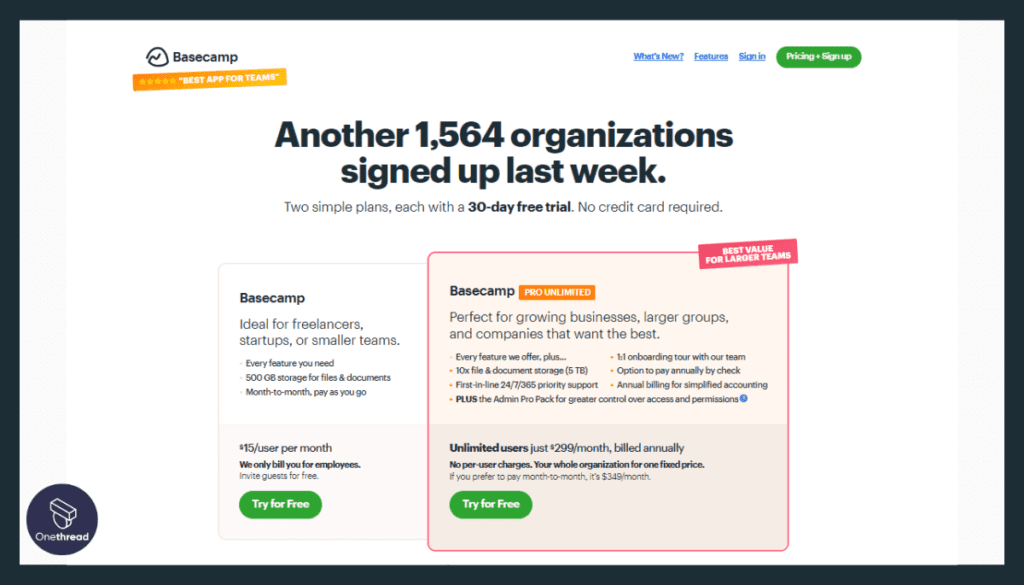
- Basecamp offers a flat pricing structure of $99 monthly for unlimited users.
11. Jira
Jira is primarily used for software development and issue tracking, but it also serves as a powerful tool for asynchronous communication. It enables teams to track and manage tasks, report bugs, and collaborate on projects efficiently.
Key Features:
- Issue tracking and project management
- Customizable workflows and task assignment
- Integration with development tools and software
Pricing:
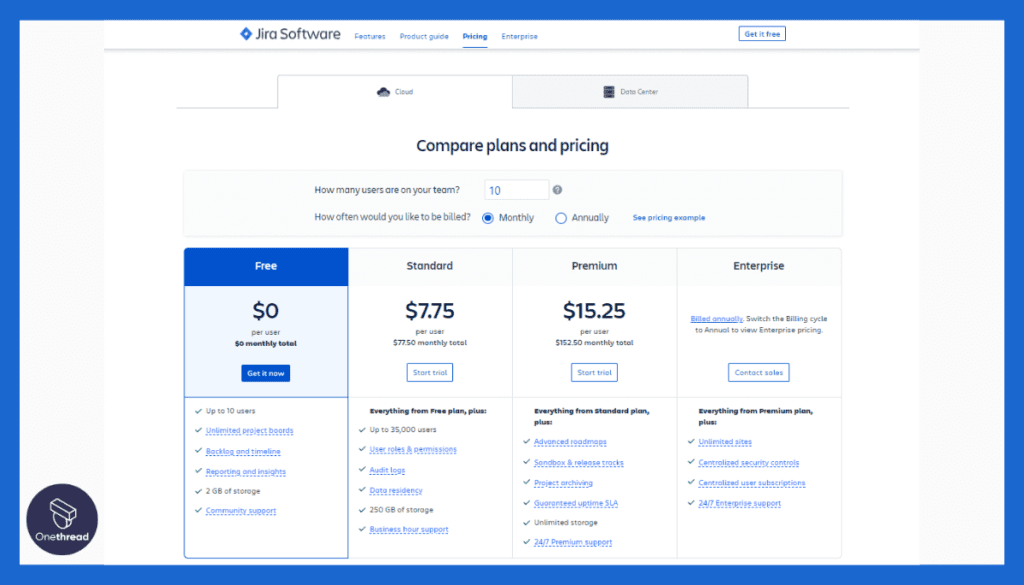
- Jira offers various pricing plans depending on the number of users and features required. Prices start at $10 per user per month.
12. Zoom
Zoom is a widely-used video conferencing tool that facilitates real-time communication and collaboration. While it is primarily designed for synchronous communication, it also allows for the recording and playback of meetings, enabling users to catch up on missed discussions asynchronously.
Key Features:
- Video and audio conferencing
- Screen sharing and remote-control capabilities
- Recording and playback of meetings
Pricing:
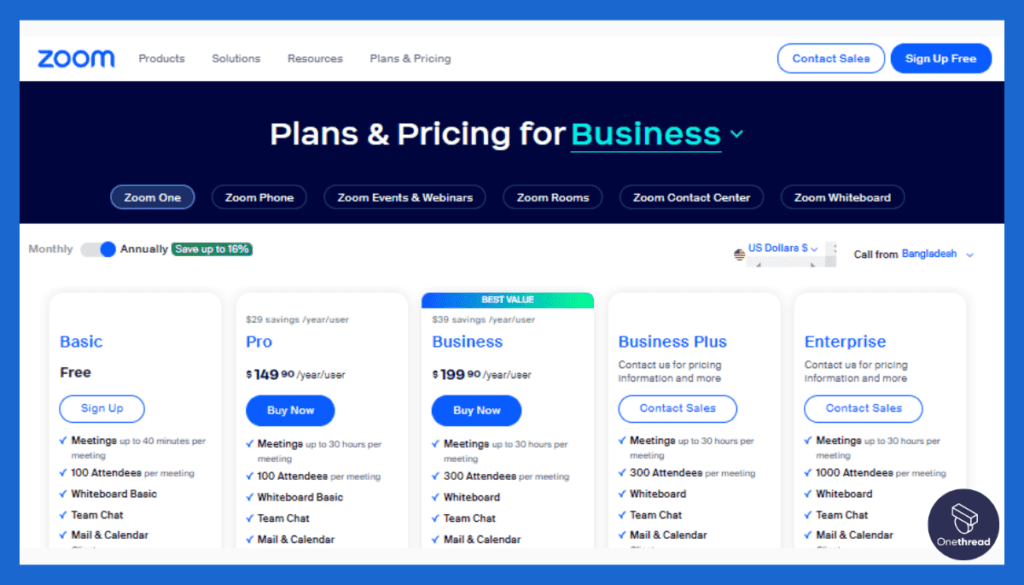
- Zoom offers a free plan with limited meeting durations and features. Paid plans, including more advanced features and larger meeting capacities, start at $14.99 per host per month.
Top Asynchronous Communication Tools at A Glance
Tool | Key Features | Pricing |
 | - Sequential task execution - Task Management for Autonomy and Flexibility - Real-time Messaging for Fluid Discussions - Collaborative Document Sharing and Editing - Notifications and Reminders for Time Management - Data Visualization for Insights Across Time Zones | Starter: Free Forever Growth: $3.00/user/month (billed annually) Scale: $6:00 BDT/user/month (billed annually) Enterprise: Contact for Quote |
 | - Cloud-based storage and collaboration - Real-time collaboration | Free: 15 GB Paid: From $1.99/month (100 GB) |
 | - Video messaging and recording - Screen and video recording - Instant sharing and commenting | Free (Limited) Paid: From $8/month per user |
 | - Knowledge management and documentation - Team collaboration and sharing - Version control and search functionality | Free (Limited) Paid: From $6/user/month |
 | - Internal knowledge base - Team documentation and collaboration - Integration with popular tools | Free Trial Paid: From $5/user/month |
 | - Chat-based collaboration - Video and audio conferencing - Integration with Office apps | Free (Limited) Paid: From $5/user/month |
 | - Direct messaging and group chats - Integration with Google apps | Free (Google Workspace) Paid: From $6/user/month |
 | - Task management and assignment - Collaboration on project discussions - File sharing and organization | Free (Basic) Paid: From $10.99/user/month |
 | - Visual task boards - Task assignment and due dates - Integration with productivity tools | Free (Basic) Paid: From $12.50/user/month |
 | - Message boards for team discussions - Task tracking and assignment - Document and file sharing | $99/month (Unlimited Users) |
 | - Issue tracking and project management - Customizable workflows - Integration with development tools | From $10/user/month |
 | - Video and audio conferencing - Screen sharing and recording - Recording and playback of | Free (Limited) Paid: From $14.99/host/month |
Tips to Use Asynchronous Communication Effectively
Here are 10 tips to help you use asynchronous communication effectively:
- Choose the right tool: Select a communication tool that suits your team’s needs and preferences. Consider factors such as ease of use, features, and integration capabilities.
- Set clear expectations: Establish guidelines and expectations for asynchronous communication within your team. Define response times, preferred communication channels, and appropriate tool use.
- Be concise and to the point: Asynchronous communication often involves written messages. Keep your messages concise and focused to ensure they are easily understood and actionable.
- Use subject lines effectively: When sending emails or messages, utilize clear and descriptive subject lines. This helps recipients quickly understand the content and priority of the communication.
- Structure your messages: Organize your messages in a logical and structured manner. Use bullet points, headings, or numbered lists to make it easier for others to follow and respond.
- Consider time zones and schedules: If you work with a distributed team across different time zones, be mindful when sending messages. Avoid expecting immediate responses when it may be outside someone’s working hours.
- Utilize tagging or @mentions: When using tools that support tagging or @mentions, use them to grab specific team members’ attention. This ensures that relevant individuals are notified and can respond promptly.
- Be mindful of tone and clarity: In written communication, it can be challenging to convey tone and nuances. Take care to write, use appropriate language, and consider how others may interpret your message.
- Practice active listening: Even in asynchronous communication, active listening is important. Take the time to read and understand messages thoroughly before responding. This helps avoid misunderstandings and promotes effective collaboration.
- Follow up and provide updates: Follow up appropriately if a discussion or task requires further input or progress. Provide updates, summarize decisions made, and ensure everyone involved is informed.
What are the Best practices for asynchronous Communication?
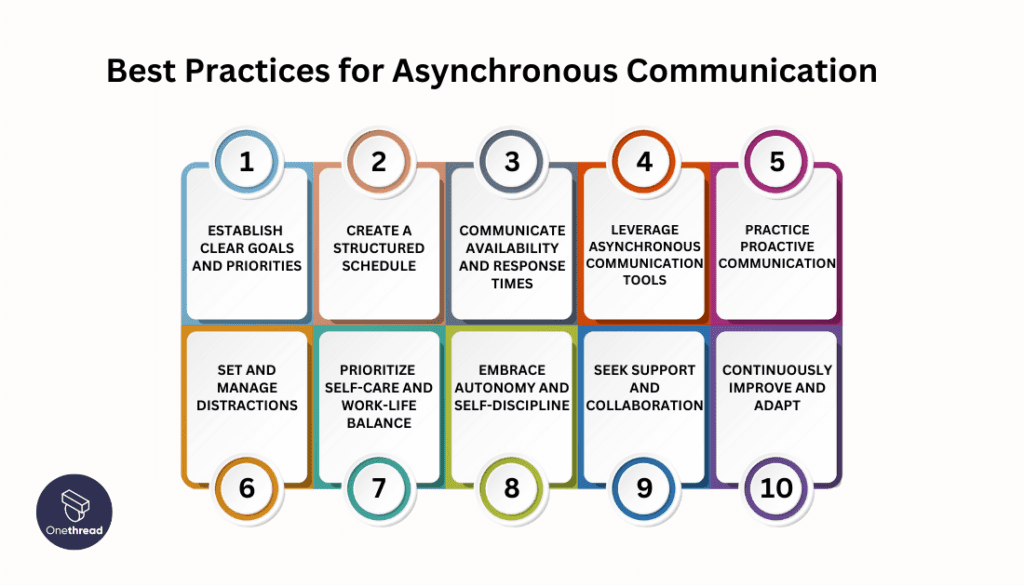
Best practices for asynchronous workers, who operate independently and remotely, include:
- Establish clear goals and priorities: Set objectives and prioritize tasks to stay focused and productive. This helps maintain a sense of direction and ensures that work aligns with team and organizational goals.
- Create a structured schedule: Develop one that suits your productivity patterns and preferences. Establish specific working hours or time blocks dedicated to your tasks, and communicate this with your team.
- Communicate availability and response times: Communicate your availability and response times to team members. Let them know when you are actively working and when they can expect a response. This helps manage expectations and promotes effective collaboration.
- Leverage asynchronous communication tools: Utilize the appropriate tools and technologies for asynchronous communication, such as email, chat platforms, project management software, and document collaboration tools. Familiarize yourself with their features and functionalities to maximize their effectiveness.
- Practice proactive communication: Take the initiative to provide your team with regular updates and progress reports. Share completed tasks, highlight challenges, and seek input or clarification as needed. This ensures that your team stays informed and can provide support if required.
- Set and manage distractions: Establish boundaries to minimize interruptions and distractions during your designated working hours. Communicate your availability to friends, family, or roommates, and create a conducive work environment that supports your focus and productivity.
- Prioritize self-care and work-life balance: Take care of your well-being and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Practice self-care activities, set aside time for personal interests and hobbies, and establish boundaries between work and personal life to prevent burnout and promote overall well-being.
- Embrace autonomy and self-discipline: As an asynchronous worker, you have more autonomy and responsibility. Embrace this independence and practice self-discipline to manage your time effectively and meet deadlines. Set personal goals and hold yourself accountable for your work.
- Seek support and collaboration: Although asynchronous work often involves working independently, don’t hesitate to contact your team members for support, feedback, or collaboration when needed. Use synchronous communication methods, such as video calls or scheduled meetings, for more in-depth discussions or brainstorming sessions.
- Continuously improve and adapt: Regularly evaluate your workflows, tools, and strategies for asynchronous work. Identify areas for improvement and experiment with new approaches to optimize your productivity and effectiveness. Stay open to feedback and adapt your practices accordingly.
Last Notes
Asynchronous communication is the superhero of remote work and global collaboration. It allows you to connect and collaborate with others on your schedule across different time zones.
No more rushing to meetings or waiting for immediate responses. It’s like having a superpower to work at your own pace while staying connected and productive. So embrace the asynchronous way and enjoy the flexibility, focus, and efficiency it brings to your work and life. You’ve got this!
Maximize productivity with asynchronous communication. Collaborate on your own time, stay connected remotely, and work efficiently with powerful tools.
FAQ
What is asynchronous vs. synchronous?
Asynchronous communication refers to interactions that occur without real-time or simultaneous participation, allowing individuals to communicate and respond at different times. On the other hand, synchronous communication involves real-time interactions where participants engage simultaneously, such as in face-to-face conversations or video conferences.
Where is it asynchronously used?
Asynchronous communication is commonly used in various contexts, including remote work environments, distributed teams, online education, collaborative projects, and professional settings where participants are in different time zones or have varying schedules. It allows for flexibility, enables individuals to work independently, and facilitates effective collaboration across time and location barriers.
Why do we use asynchronous communication?
We use asynchronous communication for several reasons. It allows for flexibility, as participants can communicate and respond conveniently. It accommodates different time zones and schedules, promotes productivity by minimizing interruptions, enables thoughtful responses, and provides a documented record of communication for reference and clarity.
