In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly striving to stay ahead of the competition. Traditional project management approaches often fall short in meeting the demands of such an environment.
This is where Agile Project Management comes into play. Agile, with its iterative and flexible nature, has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its ability to deliver value in a rapidly changing landscape.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of Agile Project Management, exploring its values, principles, steps, and its suitability for different teams.
What Is Agile Project Management?
Agile Project Management is a dynamic and iterative approach to managing projects that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
It is a departure from traditional project management methods that follow a linear and sequential process. Agile is particularly suited for projects in fast-paced and unpredictable environments, where requirements may change frequently, and stakeholders need to be actively involved throughout the project lifecycle.
At its core, Agile Project Management focuses on delivering value to the customer in incremental stages rather than waiting for a final product. It embraces change and welcomes it as an opportunity for improvement, rather than viewing it as a disruption.
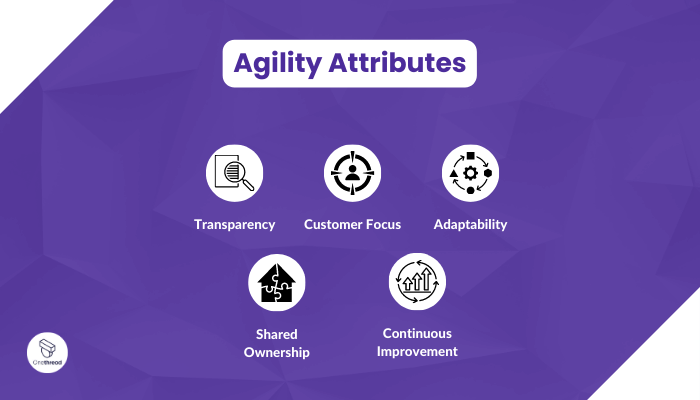
Agile teams work in short iterations and sprints, typically lasting one to four weeks, during which they plan, execute, and review their work.
One of the key principles of Agile Project Management is collaboration. Cross-functional teams work together closely, sharing knowledge, skills, and ideas to achieve project goals.
Communication is prioritized, with face-to-face interactions preferred over written documentation. This allows for quick decision-making, problem-solving, and alignment among team members.
Another essential aspect of Agile is the involvement of stakeholders throughout the project. Regular feedback and input from customers, users, and other stakeholders help shape the direction of the project and ensure that it remains aligned with their needs.
This constant engagement allows for early identification of potential issues or changes in requirements, reducing the risk of delivering a product that does not meet expectations.
Agile Project Management also emphasizes continuous improvement. At the end of each sprint, teams conduct a retrospective to reflect on their work, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. This iterative process enables teams to learn from their experiences, adapt their approach, and enhance their performance in subsequent sprints.
What are the 4 Core Values of Agile?
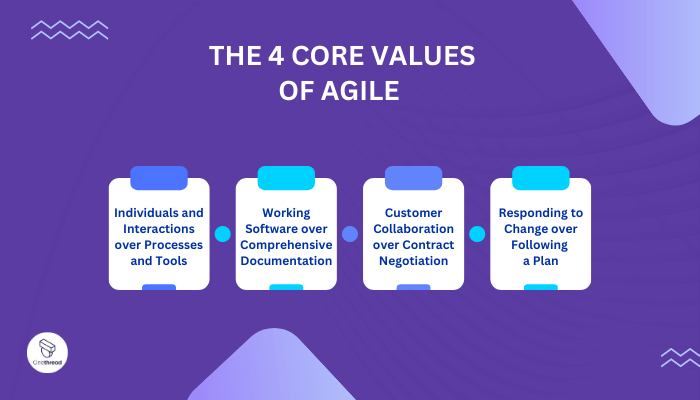
Agile Project Management is founded upon four fundamental values that not only shape its philosophy but also serve as guiding principles for its practices. These values are essential in fostering a collaborative and adaptive approach to project management. Let’s delve deeper into each of these core values and understand their significance in Agile.
- Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools
Agile recognizes that the success of a project lies in the effectiveness of communication and collaboration among team members.
While processes and tools are important, they should not overshadow the importance of human interaction. Agile teams prioritize creating an environment where open and transparent communication thrives, enabling team members to share ideas, resolve conflicts, and collectively drive the project forward.
- Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation
Agile places a higher emphasis on delivering a functional product rather than drowning in excessive documentation. While documentation is necessary for maintaining project records and knowledge sharing, Agile teams understand that the ultimate goal is to provide tangible value to the end user.
By focusing on creating working software early and frequently, Agile teams can gather valuable feedback, incorporate necessary changes, and ensure that the product aligns with customer expectations.
- Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation
In Agile Project Management, the active involvement of customers throughout the project is vital. Instead of relying solely on contract negotiations, Agile teams actively collaborate with customers to gain a deep understanding of their needs, preferences, and expectations.
This collaborative approach helps in building a strong partnership between the team and the customer, resulting in a product that truly meets the customer’s requirements and provides maximum value.
- Responding to Change over Following a Plan
Change is inevitable in any project, and Agile embraces this reality. Unlike traditional project management methods that adhere strictly to a predefined plan, Agile encourages teams to be adaptable and responsive to change. Agile teams understand that requirements evolve, market conditions fluctuate, and new insights emerge over time.
By embracing change and maintaining flexibility, Agile teams can quickly adapt their plans and strategies to ensure that the project stays on track and delivers the maximum value to the customer.
These four core values are the foundation of Agile Project Management, guiding teams to prioritize collaboration, working software, customer collaboration, and adaptability. By internalizing and applying these values, Agile teams can effectively navigate the complexities of modern projects and achieve greater success.
What are the 12 principles of Agile project management?
Agile Project Management is guided by a set of principles that serve as the bedrock for its practices and reinforce its core values. These principles, when implemented, enable teams to effectively navigate the complexities of projects and achieve success.
Let’s delve into each of these principles and understand their significance in Agile Project Management.
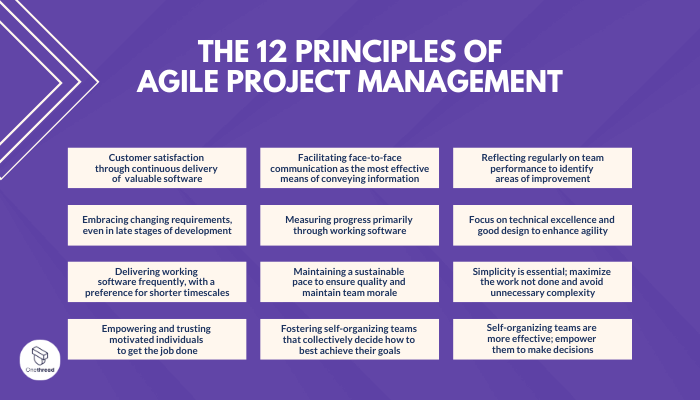
- Customer satisfaction through continuous delivery of valuable software
Agile places great emphasis on delivering value to the customer. By continuously delivering working software that meets the customer’s needs, Agile teams can ensure customer satisfaction and build strong relationships.
- Embracing changing requirements, even in the late stages of development
Agile acknowledges that requirements can change throughout the project lifecycle. Instead of resisting change, Agile teams embrace it and adjust their plans accordingly. This flexibility allows for better adaptation to evolving market demands.
- Delivering working software frequently, with a preference for shorter timescales
Agile encourages teams to deliver tangible results frequently, typically in short iterations and sprints. This iterative approach enables teams to gather feedback early, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the software meets customer expectations.
- Empowering and trusting motivated individuals to get the job done
Agile promotes a culture of trust, empowerment, and accountability. By trusting motivated individuals to take ownership of their work, teams can foster a sense of ownership and promote collaboration, resulting in higher productivity and quality.
- Facilitating face-to-face communication as the most effective means of conveying information
Agile recognizes that effective communication is vital for project success. While tools and documentation are important, Agile teams prioritize face-to-face communication as it allows for immediate clarification, quicker decision-making, and better alignment among team members.
- Measuring progress primarily through working software
Agile focuses on tangible outcomes rather than relying solely on traditional project metrics. By measuring progress based on working software, teams can ensure that they are delivering value and meeting the project’s objectives.
- Maintaining a sustainable pace to ensure quality and maintain team morale
Agile teams understand the importance of maintaining a sustainable pace of work. By avoiding excessive workloads and burnout, teams can sustain their productivity, deliver high-quality software, and maintain positive team morale.
- Fostering self-organizing teams that collectively decide how to best achieve their goals
Agile promotes self-organizing teams that are empowered to make decisions. This allows teams to capitalize on their collective knowledge and expertise, fostering innovation, creativity, and ownership of the project’s success.
- Reflecting regularly on team performance to identify areas of improvement
Agile encourages teams to regularly reflect on their performance and identify areas for improvement. By conducting retrospectives, teams can learn from their experiences, address challenges, and continuously enhance their processes and practices.
- Focus on technical excellence and good design to enhance agility
Agile encourages continuous attention to technical excellence and maintaining clean code. This approach makes it easier to adapt to changes and reduces technical debt.
- Simplicity is essential; maximize the work not done and avoid unnecessary complexity
Agile projects prioritize simplicity to reduce overhead and streamline processes. Focusing on crucial features and minimizing unnecessary work leads to efficient outcomes.
- Self-organizing teams are more effective; empower them to make decisions
Agile teams are encouraged to be self-organizing and take ownership of their work. Empowering teams to make decisions promotes creativity and adaptability.
What Are The Agile Project Management Steps?
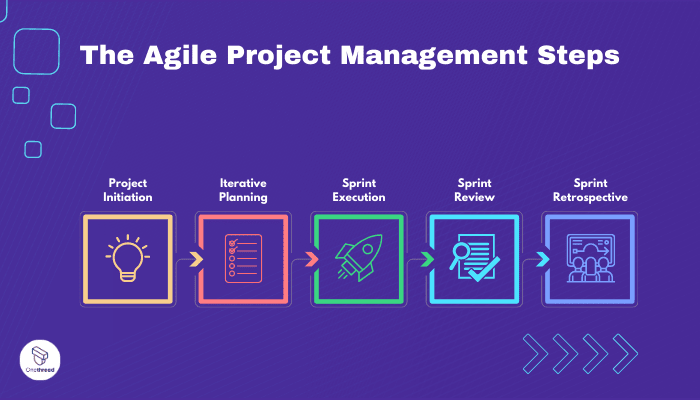
Agile Project Management follows a cyclical process that consists of several key steps. Let’s expand on each of these steps to understand their significance and how they contribute to the overall success of Agile projects.
- Project Initiation
During the project initiation phase, the objectives, scope, and desired outcomes of the project are clearly defined. This step involves identifying the key stakeholders and establishing a shared understanding of the project’s goals. By setting a solid foundation, Agile teams can align their efforts and ensure everyone is working towards a common vision.
- Iterative Planning
Agile projects are broken down into smaller iterations and sprints. In the iterative planning phase, the team prioritizes the tasks and creates a backlog of work to be completed. The backlog serves as a dynamic list that evolves and adjusts as the project progresses, allowing the team to adapt to changing requirements and priorities.
- Sprint Execution
The sprint execution phase is where the actual work takes place. The team collaboratively works on the tasks defined in the sprint backlog. Agile teams emphasize collaboration, adaptability, and delivering value to the customer.
They focus on regular communication and continuous feedback, ensuring that the work remains aligned with the project’s goals and meets the customer’s expectations.
- Sprint Review
At the end of each sprint, a sprint review is conducted to evaluate the completed work. The team showcases the deliverables to the stakeholders and gathers their feedback.
This feedback is invaluable as it helps the team understand if they are on the right track and if any adjustments or improvements are needed. The insights gained from the sprint review feed into the planning for the subsequent sprints.
- Sprint Retrospective
The sprint retrospective is a crucial step for continuous improvement. During this phase, the team reflects on their performance, identifies areas for improvement, and celebrates successes.
The retrospective encourages open and honest communication, enabling the team to learn from their experiences and make adjustments to enhance their processes, collaboration, and overall performance.
By following this cyclical process, Agile Project Management allows teams to adapt to changing requirements, deliver value in incremental stages, and continuously improve their performance.
The iterative nature of Agile ensures that feedback is incorporated throughout the project, reducing risks and increasing the likelihood of success. The focus on collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement sets Agile apart from traditional project management approaches and makes it well-suited for dynamic and complex projects.
Traditional Project Management Vs Agile Project Management
Here’s our comparison view between Traditional Project Management and Agile Project Management:
Traditional Project Management
- Linear and Sequential: Traditional project management follows a linear and sequential approach, with a clear distinction between project phases (such as initiation, planning, execution, and closure). Each phase is typically completed before moving on to the next.
- Emphasis on Documentation: Traditional project management places a significant emphasis on comprehensive documentation, including detailed project plans, requirements documents, and progress reports. Extensive documentation is seen as necessary for project control and stakeholder communication.
- Predictive Planning: Traditional project management relies on detailed upfront planning, aiming to define the project scope, timeline, and deliverables as accurately as possible. This approach assumes that requirements will remain relatively stable throughout the project.
- Fixed Scope and Schedule: Traditional project management typically operates under fixed scope and schedule constraints. Any changes to the project scope or schedule are carefully evaluated and often require formal change management processes.
- Centralized Decision-Making: Decision-making in traditional project management is typically centralized, with project managers and stakeholders making key decisions. Communication channels may follow a hierarchical structure.
Agile Project Management
- Iterative and Incremental: Agile project management follows an iterative and incremental approach. Each sprint delivers a working product increment, allowing for continuous feedback and adaptation.
- Value over Documentation: Agile project management values working software over excessive documentation. While documentation still exists, the focus is on delivering tangible value to the customer through frequent iterations.
- Adaptive Planning: Agile project management embraces change and adapts to evolving requirements. Planning is done at multiple levels, with high-level plans initially defined and detailed plans refined as the project progresses.
- Flexible Scope and Schedule: Agile project management accommodates changes in scope and schedule, allowing for flexibility based on customer feedback and changing priorities. The focus is on delivering the highest value features and adapting to emerging needs.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Agile project management promotes decentralized decision-making, with self-organizing teams empowered to make decisions collectively. Communication channels encourage collaboration and transparency.
Traditional vs Agile Project Management: At A Glance
Aspect | Traditional Project Management | Agile Project Management |
Approach | Linear and Sequential | Iterative and Incremental |
Documentation Emphasis | Comprehensive Documentation | Value over Documentation |
Planning Strategy | Predictive Planning | Adaptive Planning |
Scope and Schedule Flexibility | Fixed Scope and Schedule Constraints | Flexible Scope and Schedule |
Decision-Making Structure | Centralized Decision-Making | Decentralized Decision-Making |
Phases and Execution | Clear Distinction between Phases | Continuous Feedback and Adaptation |
Stakeholder Communication | Documentation for Project Control | Value-Oriented Customer Feedback |
Change Adaptation | Limited Scope Changes Allowed | Embraces Change and Evolving Needs |
Formal Change Management Process | Required for Scope/Schedule Changes | Flexible and Iterative Approach |
Decision-Making Empowerment | Centralized Decision-Making | Decentralized and Collaborative |
Why Agile Project Management Might Not Be Right For Your Team?
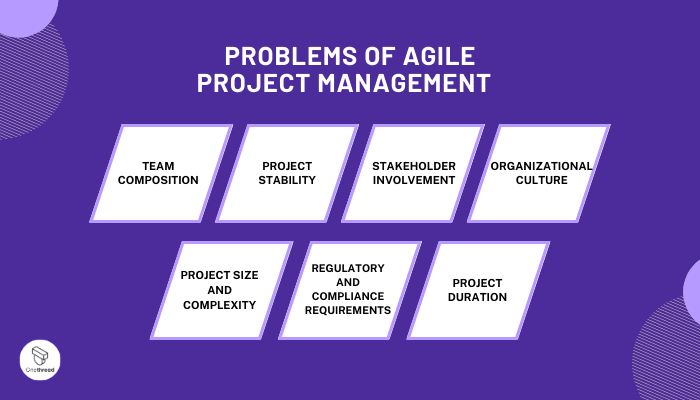
Agile Project Management, while widely adopted and successful in many contexts, may not always be the optimal approach for every team or project. Several factors should be considered when determining if Agile is the right fit. Let’s expand on each of these factors to gain a better understanding:
- Team Composition
Agile relies on self-organizing, cross-functional teams that work collaboratively to deliver value. If your team lacks the necessary skills or experiences, or if team members are resistant to change and collaboration, adopting Agile may face challenges. Assessing the team’s capabilities and willingness to embrace Agile practices is crucial before deciding to implement it.
- Project Stability
Agile is designed to handle projects with dynamic and evolving requirements. If your project has well-defined and stable requirements, a traditional project management approach may be more appropriate. Agile thrives in environments where change is expected, and the ability to adapt quickly to shifting priorities is critical for success.
- Stakeholder Involvement
Active stakeholder involvement is a cornerstone of Agile Project Management. Agile teams rely on frequent feedback from stakeholders to ensure the delivered product meets their needs and expectations.
If stakeholders are unavailable, uninterested, or unable to participate actively in the project, the benefits of Agile may be diminished. Assessing the level of stakeholder engagement and their willingness to collaborate throughout the project is essential.
- Organizational Culture
Agile Project Management is not just a methodology; it requires a supportive organizational culture. Agile values transparency, trust, and open communication among team members and stakeholders.
If your organization’s culture does not align with these values, implementing Agile may encounter resistance or challenges. Assessing the existing culture and readiness to embrace Agile principles can help determine the feasibility of adopting Agile practices.
- Project Size and Complexity
While Agile is effective for small to medium-sized projects with moderate complexity, it may not be suitable for large-scale projects with high complexity.
Assess the scale and complexity of your project to ensure that Agile methodologies can adequately address the challenges and provide the desired benefits.
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Certain industries or projects have strict regulatory and compliance requirements. Agile’s iterative and adaptive nature may pose challenges in meeting these requirements, which often demand comprehensive upfront planning and documentation. Assess the extent of regulatory and compliance constraints on your project to determine if Agile can effectively meet those requirements.
- Project Duration
Agile projects are typically executed in shorter iterations or sprints, delivering value incrementally. If your project has a significantly long duration, Agile may require additional planning and adjustments to ensure that the project remains on track and delivers value throughout the entire duration.
Some Statistics Of Agile Project Management
- According to the 14th Annual State of Agile Report, 95% of respondents stated that their organizations practiced Agile methodologies.
- A study by McKinsey & Company revealed that Agile organizations are 1.5 times more likely to be top quartile financial performers.
- The Standish Group’s CHAOS Report highlighted that Agile projects have a significantly higher success rate compared to traditional projects.
How Onethread can help in Agile Project Management?
Onethread can be a valuable tool in Agile project management by providing features and functionalities that support collaboration, communication, and efficient project execution. Here’s how Onethread can help:
- Collaborative Environment: Onethread provides a collaborative platform where team members, stakeholders, and product owners can communicate effectively. It facilitates real-time discussions, document sharing, and feedback loops, enhancing teamwork and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Agile Planning and Scheduling: Onethread allows teams to create and manage Agile project plans and schedules. Users can break down projects into tasks, set priorities, and assign responsibilities, enabling a clear understanding of project progress and goals.
- Task Tracking and Visibility: With Onethread, teams can track the status of tasks and monitor progress visually. Agile boards or task lists can be utilized to see the current state of work, identify blockers, and prioritize tasks for efficient execution.
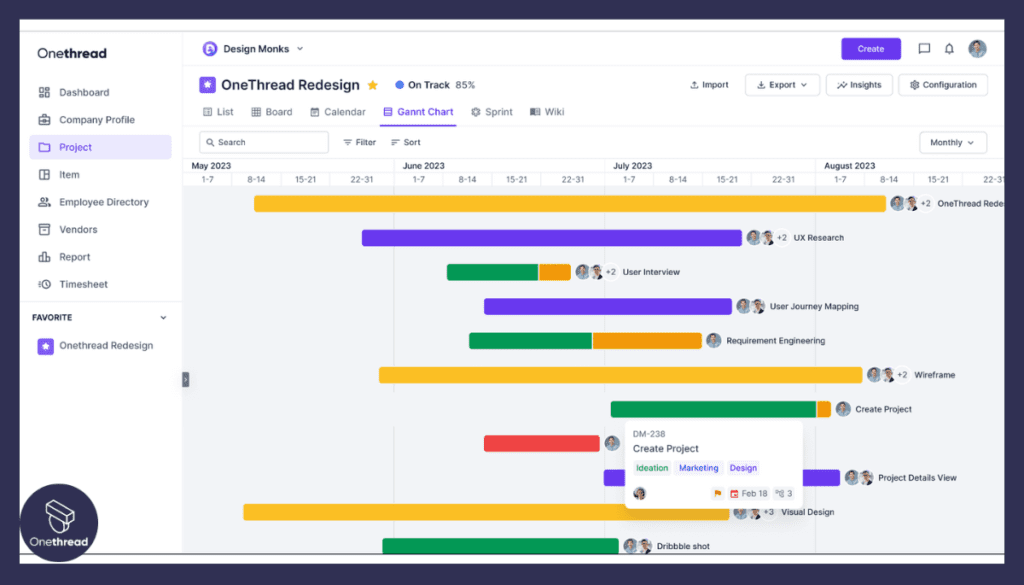
- Backlog Management: Onethread can serve as a backlog management tool, helping teams organize and prioritize product backlog items. This ensures that the most valuable features are developed early and that the backlog stays aligned with changing requirements.
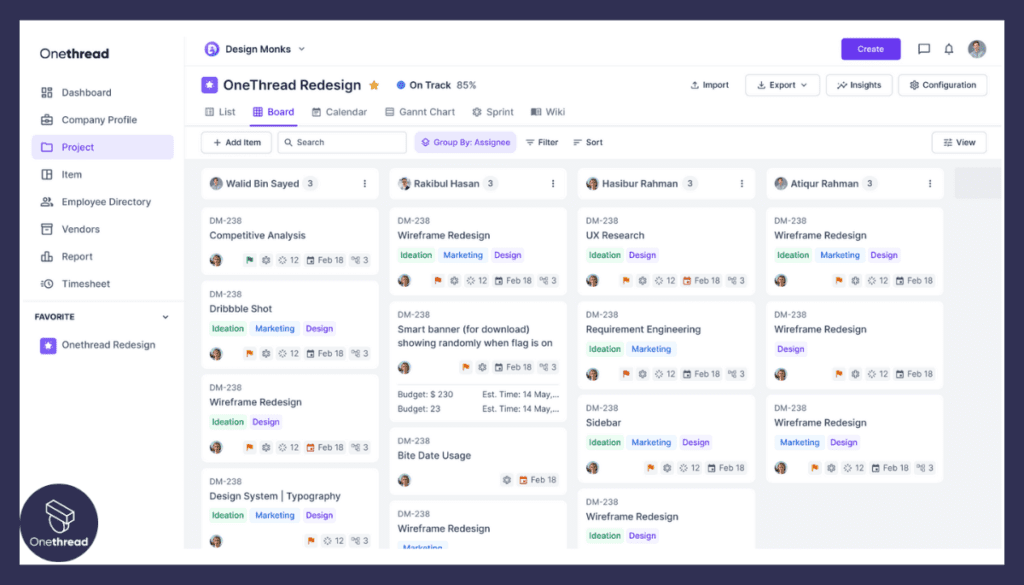
- Daily Stand-ups and Updates: Onethread facilitates daily stand-up meetings, whether in-person or virtual. Team members can share updates on progress, discuss challenges, and plan for the day, fostering effective communication and transparency.
- Visualizations and Reporting: Onethread provides visualizations such as burndown charts and velocity metrics to help teams track progress over time. These insights enable data-driven decision-making and facilitate continuous improvement.
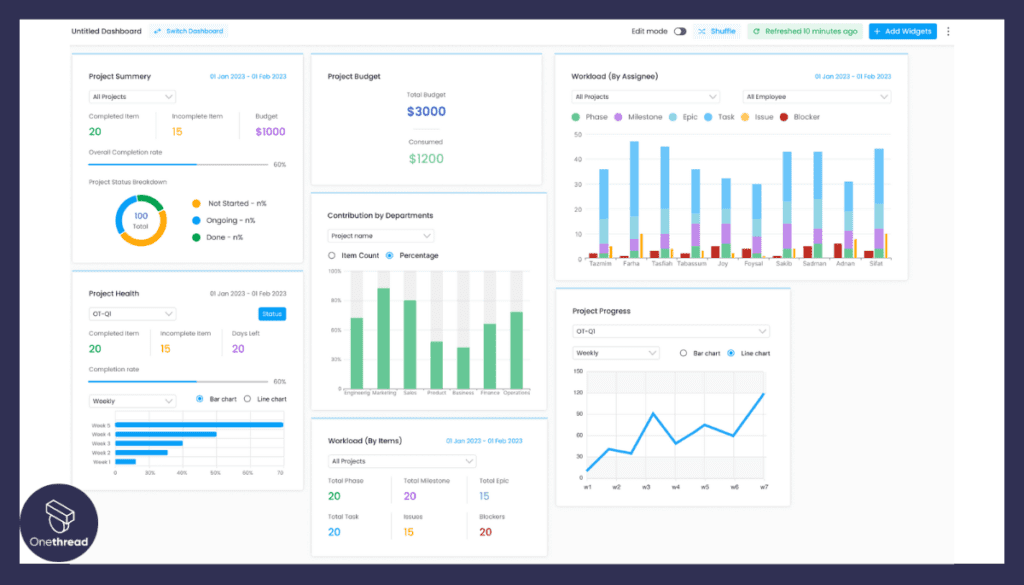
- Feedback and Iteration: Onethread enables teams to gather feedback from stakeholders and customers directly within the platform. This feedback loop facilitates quick iterations and allows teams to adapt to changing requirements.
Conclusion
Agile Project Management offers a flexible and iterative approach to project management, aligning well with the demands of today’s fast-paced business landscape. By embracing its values, principles, and steps, teams can foster collaboration, deliver value, and adapt to change more effectively.
However, it is essential to assess team composition, project stability, stakeholder involvement, and organizational culture before deciding if Agile is the right fit for your team. With careful consideration and proper implementation, Agile Project Management can empower your team to achieve success and deliver exceptional results.