In every aspect of human civilization, leadership plays a pivotal role in guiding individuals, teams, organizations, and even nations toward success and growth. A leader’s ability to inspire, influence, and direct others can have a profound impact on the achievement of collective goals and the overall well-being of those under their guidance.
However, not all leaders approach their responsibilities in the same way. Instead, they often adopt distinct leadership styles that define their approach to decision-making, communication, and team management.
Understanding different leadership styles is crucial for aspiring leaders, followers, and organizational stakeholders alike. By gaining insight into these various approaches, individuals can better comprehend their own leadership tendencies and develop the flexibility to adapt their style to suit different situations and challenges.
This article delves into an exploration of prominent leadership styles, shedding light on their defining characteristics and real-world applications. From the autocratic and democratic styles to transformational and servant leadership, each approach offers valuable insights into the dynamics of leadership and its far-reaching implications.
What are Leadership Styles?
Leadership styles refer to the distinct approaches and behaviors that leaders employ when guiding and influencing their team members or followers to achieve specific goals or objectives. A leadership style encompasses how a leader communicates, makes decisions, motivates, and manages their team.
Different situations and circumstances may call for different leadership styles, and effective leaders often adapt their approach based on the needs of the organization, the team, and the tasks at hand. There are various leadership styles, each with its unique characteristics and effects on team dynamics.
Each leadership style has its advantages and limitations, and the most effective leaders often exhibit a mix of these styles, depending on the context and the individuals they lead. The ability to flexibly employ different leadership styles allows leaders to respond effectively to a variety of challenges and lead diverse teams to success.
Why Does Your Leadership Style Matter?

Leadership styles matter for several critical reasons, as they significantly influence the overall effectiveness and success of a team, organization, or group. Here are some key reasons why leadership styles are important:
Impact on Team Employees
The leadership style a leader adopts can directly impact the performance of their team. Effective leadership can inspire and motivate team members, leading to increased productivity, better problem-solving, and higher-quality work output.
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
Different leadership styles can evoke different emotional responses from team members. A positive and supportive leadership style can foster a sense of belonging and job satisfaction, leading to higher employee engagement and reduced turnover.
Communication and Decision-making
Leadership styles affect how information is communicated within the team and how decisions are made. Open and transparent communication in democratic or participative leadership styles can lead to better collaboration and a more inclusive decision-making process.
Adaptability to Situations
Different situations may require different leadership approaches. A leader’s ability to adapt their style to suit the context can enhance their effectiveness in handling various challenges and changes that arise in the workplace.
Organizational Culture
Leadership styles significantly influence the culture of an organization. For instance, a transformational leader can instill a culture of innovation and growth, while a transactional leader might foster a culture focused on achieving specific targets.
Employee Development
Some leadership styles, such as servant leadership, prioritize the growth and development of team members. These leaders invest in their employees’ skills and career advancement, creating a more skilled and motivated workforce.
Conflict Resolution
Different leadership styles may handle conflicts and disagreements in diverse ways. Leaders with strong conflict resolution skills can effectively manage and resolve disputes within the team, preventing them from escalating and negatively affecting team dynamics.
Building Trust and Relationships in Business
Leadership styles can influence the level of trust team members have in their leader. Trust is essential for building strong relationships within the team and fostering a collaborative work environment.
Overall, leadership styles are a critical factor in shaping the culture, performance, and overall success of a team or organization. Leaders who understand the importance of different leadership styles and are willing to adapt their approach to suit the needs of their team and organization are more likely to achieve positive outcomes and foster a thriving work environment.
What Are the Top Strengths of Distinguished Leaders?

Distinguished leaders often possess a combination of various strengths that set them apart and contribute to their effectiveness and success. While individual leaders may have different strengths, some common traits and abilities exhibited by distinguished leaders include:
Visionary Thinking
Distinguished leaders have a clear and compelling vision for the future of their organization or team. They can articulate this vision to others and inspire their team to work towards shared goals.
Emotional Intelligence
Exceptional leaders are emotionally intelligent, meaning they can understand and manage their own emotions and empathize with the feelings of others. This skill allows them to build strong relationships, resolve conflicts, and create a positive work environment.
Effective Communication
Distinguished leaders are exceptional communicators. They can convey their ideas, expectations, and goals clearly and listen actively to their team members’ input and feedback.
Decisiveness
Successful leaders can make timely and well-informed decisions, even in high-pressure situations. They weigh the available information and take calculated risks when necessary.
Adapting Styles
Distinguished leaders are adaptable and can navigate through changes and uncertainties. They remain flexible in their approach and can adjust their strategies as needed to address evolving challenges.
Integrity
Highly regarded leaders demonstrate strong ethical principles and honesty. They act with integrity, which builds trust among their team and stakeholders.
Empowerment
Exceptional leaders empower their team members by delegating authority and responsibility appropriately. They trust their team’s abilities, take action accordingly, and encourage them to take ownership of their work.
Resilience
Distinguished leaders display resilience in the face of setbacks or failures. They bounce back from challenges, learn from their experiences, and maintain a positive attitude.
These strengths, combined with the ability to adapt their leadership style to different situations, contribute to the effectiveness and impact of distinguished leaders, enabling them to lead their organizations to success and create a positive and productive work environment.
10 Most Common Leadership Styles
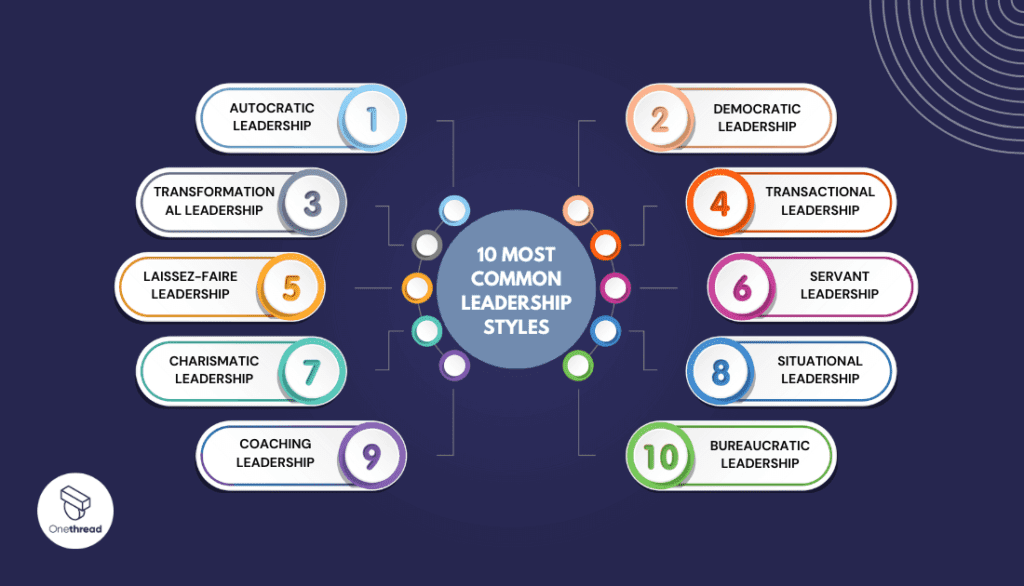
The most common leadership styles are varied, and different experts and researchers may categorize them slightly differently. However, the following ten leadership styles are commonly recognized and observed in various organizational settings:
Autocratic Leadership
An autocratic leader exercises complete control over decision-making and rarely involves team members in the process. They make decisions independently and expect strict compliance from their team.
Democratic Leadership
In contrast to autocratic leadership, democratic leaders involve team members in decision-making. They promote transparent dialogue, actively solicit feedback from their team members, and prioritize group perspectives when making decisions.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their team by articulating a compelling vision. They use their charisma and enthusiasm to energize and empower their followers to reach higher levels of performance.
Transactional Leadership Approach
Transactional leaders concentrate on establishing precise team objectives and expectations. They employ rewards and penalties to drive employee motivation, providing incentives for target achievement and repercussions for not meeting them.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leaders adopt a hands-off approach, providing their team members with a high degree of autonomy and decision-making authority. They offer minimal guidance and trust their team’s expertise.
Servant Leadership
Servant leaders prioritize the needs of their team members above their own. They actively support the personal growth and development of their followers and aim to create a positive and supportive work environment.
Charismatic Leadership
Charismatic leaders rely on their charm, personality, and communication skills to attract and influence followers. They can motivate others through their strong presence and persuasive abilities.
Situational Leadership Approach
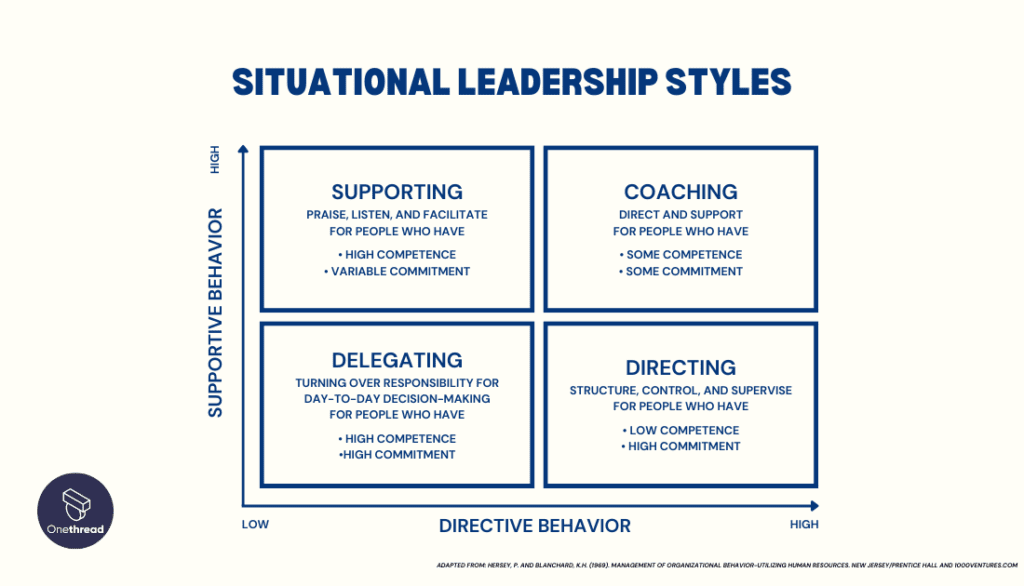
Situational leaders adapt their leadership style according to their team members’ preparedness and proficiency. They offer varying degrees of direction and assistance, tailoring their approach to each situation and the requirements of their followers.
Coaching Leadership
Coaching leaders focus on developing the skills and abilities of their team members. They provide guidance, feedback, and mentorship to help their followers improve their performance.
Bureaucratic Leadership
Bureaucratic leaders adhere strictly to established rules, policies, and procedures. They ensure that the organization operates within set parameters, which can provide stability but may limit innovation and adaptability.
It’s important to note that effective leaders often display a mix of different leadership styles, adapting their approach in accordance with the requirements of their teamand the specific circumstances they encounter. The most successful leaders can flexibly switch between these styles to create a positive and productive work environment and achieve the organization’s goals.
How Do You Know Which Leadership Style Suits You the Most?
Discovering which leadership style suits you best involves a process of self-awareness, reflection, and observation. Here are some steps to help you identify the leadership style that aligns with your personality, strengths, and values:
Self-Assessment
Start by conducting a self-assessment to understand your personality traits, management style, strengths, weaknesses, and values. Reflect on your past experiences as a leader or in positions of authority and identify instances where you felt most comfortable and effective.
Seek Feedback
Ask for feedback from colleagues, team members, or mentors about your leadership style. Their perspectives can provide valuable insights into how others perceive your leadership view and its impact on the team.
Identify Your Core Values
Clarify your core values and what you believe makes a leader effective. Consider the principles and ethics that guide your decision-making and how they align with different leadership styles.
Understand Different Leadership Styles
Familiarize yourself with the various leadership styles discussed earlier (autocratic, democratic, transformational, etc.). Understand their characteristics, strengths, and potential limitations.
Reflect on Your Goals
Consider the goals you aim to achieve as a leader. Different leadership styles may be more suitable for specific situations or objectives. Assess how each style may help you achieve your leadership goals.
Assess Your Team
Understand the dynamics and composition of your team or the people you will be leading. Different team members may respond differently to various leadership styles, and a flexible approach might be necessary.
Test and Adapt
Try different leadership styles in different situations. Pay attention to how you and your team respond to each approach. Be open to experimentation and be willing to adapt your style based on the needs of the situation.
Consider Development Opportunities
Engage in leadership development programs, workshops, or coaching sessions. These resources can help you explore and enhance your leadership style and skills.
Embrace Continuous Learning
Leadership is an ongoing journey of growth and improvement. Stay curious and continue learning from your experiences and the experiences of other leaders.
Reflect and Refine
Regularly reflect on your leadership experiences, successes, and challenges. Use this reflection to refine your approach and continually evolve as a leader.
Remember that leadership styles can be situational, and the most effective leaders are often those who can adapt their style to different circumstances. The key is to remain authentic to yourself and your core values while also being flexible and open to growth and improvement.
Matching Leadership Styles with Work, Projects, and Industries

Leadership styles can be adapted to various types of work, projects, and industries based on their specific needs and characteristics. Here are a few leadership styles and the contexts in which they are often suitable:
- Autocratic Leadership:
- Suitable for: High-risk industries (e.g., aviation, healthcare) where quick, decisive actions are necessary.
- When to Use: During emergencies, critical situations, or when immediate compliance is required.
- Democratic Leadership:
- Suitable for: Creative industries (e.g., design, marketing) and knowledge-based projects.
- When to Use: Team input is valuable for generating ideas, problem-solving, and fostering a sense of ownership.
- Transformational Leadership:
- Suitable for: Industries undergoing significant changes (e.g., technology, startups) or where innovation is crucial.
- When to Use: When inspiring and motivating employees to embrace change, think creatively, and achieve long-term goals.
- Transactional Leadership:
- Suitable for: Traditional industries with well-defined processes (e.g., manufacturing, finance).
- When to Use: Ensuring adherence to established procedures, managing routine tasks, and maintaining operational efficiency.
- Servant Leadership:
- Suitable for: Healthcare, education, non-profit sectors, and any industry emphasizing ethical and people-centered values.
- When to Use: When focusing on the well-being of team members, fostering a collaborative environment, and prioritizing the growth and development of individuals.
- Laissez-Faire Leadership:
- Suitable for: Highly skilled and self-motivated teams, such as research teams or creative professionals.
- When to Use: When team members are experts in their fields and require minimal guidance, and when autonomy and creative freedom are valued.
- Charismatic Leadership:
- Suitable for: Industries where inspiration and motivation play a significant role (e.g., entertainment, motivational speaking).
- When to Use: When rallying a team around a shared vision, boosting morale, and driving passion and energy are essential.
- Coaching Leadership:
- Suitable for: Industries emphasizing employee development and growth (e.g., education, professional services).
- When to Use: When guiding employees to improve their skills, providing regular feedback, and fostering individual growth and advancement.
It’s important to note that a flexible and adaptive leadership approach can be effective in many situations. Moreover, a blend of different leadership styles might be suitable depending on the specific goals, team dynamics, and stages of a project or industry trends.
Final Words
Leadership styles play a crucial role in shaping the effectiveness and success of leaders in various organizational settings. Understanding the different leadership styles and their characteristics can help individuals identify the approach that best suits their personality, strengths, and values.
A combination of self-assessment, seeking feedback, and reflection can aid in the discovery of one’s natural leadership tendencies. Leadership is not a one-size-fits-all concept, and successful leaders often adapt their style to meet the needs of their team and the challenges they face.
By recognizing and leveraging one’s strengths, a leader can create a supportive and productive work environment, inspire their team, and achieve shared goals for the organization’s success.
