Picture this: you’re sculpting a masterpiece, crafting each detail with finesse. The secret to this symphony of success? A dance of careful planning, seamless execution, and top-notch management.
Now, enter the project life cycle – your trusty compass in the vast sea of project management. Think of it as your project’s very own roadmap, guiding you from idea to reality through a series of strategic phases.
These phases? They’re like the sturdy pillars supporting your grand project architecture. They provide the backbone, the clarity, and the reins you need to steer your project ship toward triumph.
This article? Consider it your treasure map, leading you through the treasure trove of project life cycle’s five phases. We’re diving deep into each phase, uncovering its secrets, and showing you how these puzzle pieces fit together in the grand picture of project mastery.
So, fellow project navigators, are you ready to decode the art of project life cycles? Let’s embark on this voyage, unraveling the mysteries, and steering your projects to victory, one strategic phase at a time!
Understanding Project Management: A Comprehensive Overview
Project management is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses a range of activities essential for achieving specific objectives and meeting predetermined success criteria within a specified timeframe.
It involves the careful coordination of various elements, from project initiation to closure, in order to facilitate effective teamwork and project success.
Key Elements of Project Management
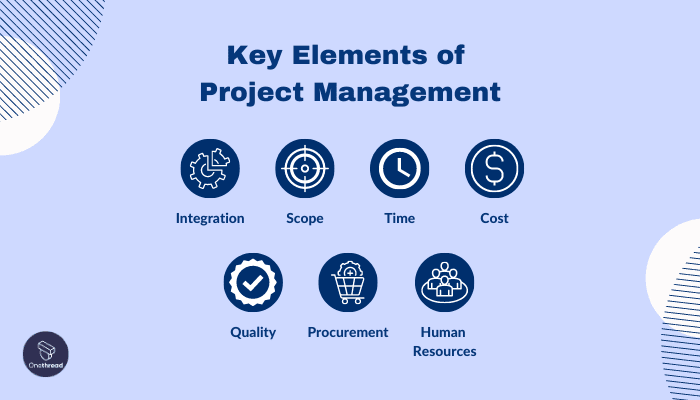
- Integration: Project management relies on the integration of different project components and activities to ensure a cohesive and synchronized approach. By harmonizing various aspects of a project, such as planning, execution, and control, integration enhances the chances of achieving project goals.
- Scope: A crucial element of project management is defining and managing the project’s scope. This involves determining the project’s boundaries, deliverables, and objectives, as well as outlining what falls within or outside the project’s scope. Effective scope management helps maintain focus and prevents scope creep.
- Time: Time management is vital in project management, as projects are typically bound by specific deadlines. Project managers must develop realistic project schedules, allocate resources efficiently, and track progress to ensure timely completion of tasks and milestones.
- Cost: Managing project costs is essential to ensure that the project remains within budget. Project managers must estimate and allocate resources effectively, monitor expenditures, and control costs throughout the project lifecycle.
- Quality: Maintaining high-quality standards is crucial to project success. Project management involves setting and adhering to quality objectives, implementing quality assurance processes, and conducting regular quality checks to ensure that deliverables meet or exceed the required standards.
- Procurement: In many projects, procuring external resources, goods, or services is necessary. Project managers are responsible for effectively managing procurement processes, which includes vendor selection, contract negotiation, and ensuring timely delivery of goods or services.
- Human Resources: Project management involves assembling and managing project teams composed of individuals with diverse skills and expertise. It includes activities such as resource allocation, team building, and fostering effective communication and collaboration among team members.
Understanding the Project Process
In project management, understanding the project process and the different phases involved is crucial for successful project implementation. The project process encompasses the entire journey of project implementation, including internal processes and actions. It involves the decision-making and execution of work instructions, procedures, network plans, and project management software by the project manager.
By overseeing these aspects, the project manager ensures smooth execution and successful completion of the project.
The PMBOK Project Management Cycle: Defining Project Phases
To effectively manage projects, it is essential to comprehend the project life cycle, which is composed of various phases. The selection of these phases is based on their alignment with the specific requirements of the project.
Elements of the project life cycle according to pmbok:
The PMBOK outlines key elements that define the project life cycle. These elements serve as guidelines for project managers to plan and execute each phase efficiently. They include:
- Work Accomplishment: Clearly defining the tasks and activities that must be completed within each project phase.
- Deliverables: Identifying the tangible outcomes or results that are expected at the completion of each phase.
- Project Team: Determining the individuals who will be involved in the project and constitute the project team.
- Monitoring and Control: Establishing mechanisms to track progress, evaluate performance, and ensure adherence to project objectives and timelines during each phase.
By considering these elements, project managers gain a comprehensive understanding of the necessary tasks, milestones, and stakeholders involved in each phase, enabling them to effectively plan and execute the project.
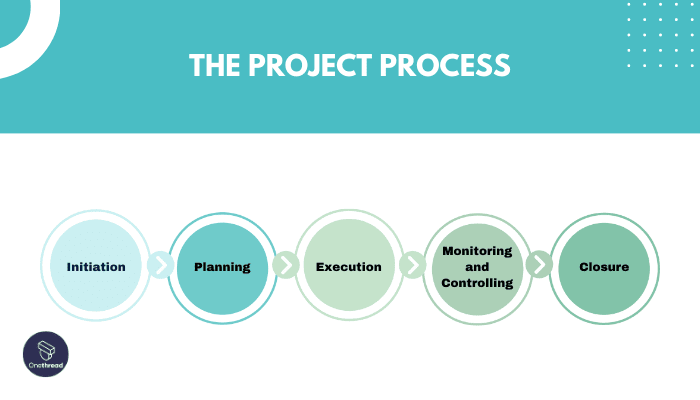
Project Life Cycle 5 Phases – Understanding The Project Life Cycle
A project phase encompasses a set of interconnected project management tasks. Typically, the phases in the project life cycle follow a sequential order, and each phase concludes with the accomplishment of one or more project deliverables.
What are the five stages of the project life cycle?
The 5 phases of project life cycle are:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Performance monitoring
- Closure
Phase 1: Project Initiation
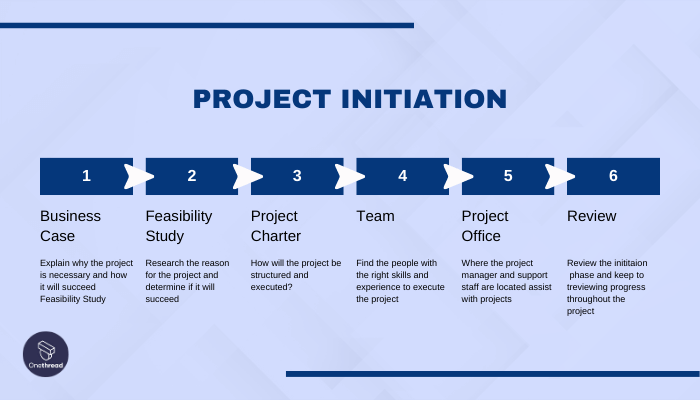
Project initiation marks the beginning of a project and involves defining its scope and objectives. During this phase, the project manager engages in a kick-off meeting with the client(s) to gain a comprehensive understanding of the project. The primary goal is to clarify project goals, objectives, and expectations.
The project manager diligently examines project details, asking relevant questions to ensure a thorough comprehension of the project’s requirements.
Key Questions Addressed in the Initiation Phase
Why this project?
The purpose and rationale behind undertaking the project are identified and clarified.
Is the project feasible?
Feasibility assessments are conducted to evaluate the project’s viability, considering factors such as resources, budget, and time constraints.
Who are the potential partners in the project?
Identifying and involving relevant stakeholders and partners is crucial for successful project execution.
What are the project boundaries?
Establishing the project’s boundaries helps define its scope and sets clear limits on what is included or excluded.
How does the end-result look like?
The desired outcome of the project is envisioned and outlined, providing a clear picture of the expected deliverables.
Project Initiation Document (PID)
Once the project receives approval, the project manager creates a Project Initiation Document (PID). This document serves as a comprehensive reference outlining the project’s purpose, requirements, and initial plan. It provides a framework for project execution and serves as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle.
Tip: Involving Technical Expertise
It is advisable to have at least one developer present during the project initiation meeting. Their presence ensures the availability of expertise to address and provide guidance on technical questions or concerns related to the project.
Phase 2: Project Planning
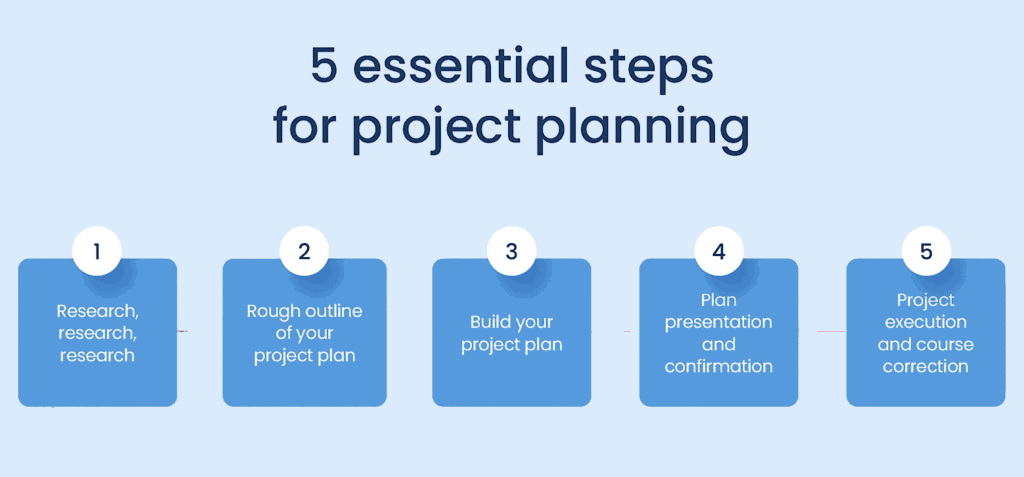
In the project planning phase, it is crucial to develop a roadmap that outlines the objectives and provides clear direction for all project members. This involves setting goals and assigning job responsibilities to ensure a coordinated effort. Many project managers utilize the S.M.A.R.T goal-setting process to establish achievable targets.
S.M.A.R.T Goals: A Strategic Approach
S.M.A.R.T goals are widely recognized as an effective goal-setting technique. By breaking down the acronym, each letter represents a quality that contributes to crafting well-defined goals.
- Specific: Goals should be clearly defined, answering the questions of what, who, where, which, when, and how.
- Measurable: Criteria should be established to measure the success and progress of each goal.
- Attainable: It is important to identify the necessary steps and resources required to achieve the goals.
- Realistic: Goals should be practical and feasible within the given constraints and time frame.
- Time-bound: A timeframe should be established for each goal to create a sense of urgency and ensure timely completion.
Challenges and Considerations
The project planning phase presents numerous challenges for project managers. They must address preconditions, functional requirements, operational requirements, and design limitations.
Additionally, this phase involves identifying the work, creating a schedule, estimating costs, and managing potential risks.
Risk Management and Accountability
During the project planning phase, it is crucial to practice effective risk management. This includes identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. Furthermore, it is important to ensure that every project member has a clear understanding of their responsibilities and is held accountable for their assigned tasks.
Tip: Efficient Scheduling
When creating a project schedule, it is advisable to keep it within a timeframe of 10 days or less. This helps maintain focus and urgency while ensuring that the project progresses smoothly. Additionally, it is essential to ensure that every project member is fully aware of their responsibilities and is committed to fulfilling them.
By following a comprehensive project planning process and incorporating S.M.A.R.T goals, project managers can set the stage for a successful project implementation.
Phase 3: Project Execution
The project execution phase marks the point where the project starts to take shape and come to life. This phase is often referred to as the “meat” of the project, as it involves a flurry of activities.
Programmers are coding, web designers are working on graphics, and project managers are creating status and performance reports. It is also known as the implementation phase.
Key Considerations in the Implementation Phase
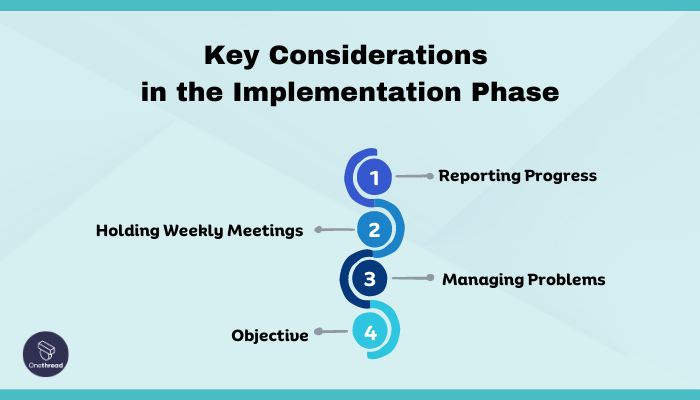
During the implementation phase, several important aspects require attention to ensure successful project execution.
- Reporting Progress: Regular updates and status reports are essential during the execution stage. Providing the required information in the appropriate format and promptly identifying and addressing issues are crucial. These resources prove valuable, particularly during times of crisis.
- Holding Weekly Meetings: Conducting weekly meetings helps maintain focus and prevents team members from deviating from essential activities. Clear agendas should be set for these meetings to maximize productivity and minimize wasted time. Team members should already be aware of the purpose of the meeting to ensure efficient utilization of everyone’s time.
- Managing Problems: As the project is in motion, encountering problems is inevitable. Issues such as quality concerns, time management difficulties, and declining team morale can pose threats to project success. Effectively managing and resolving these problems is crucial to maintain progress and achieve the desired outcomes originally agreed upon.
- Objective: The primary objective during the execution phase is to achieve results that meet the project’s requirements and align with the goals established at the outset.
Tip: Utilizing Project Management Software
Consider using project management software, such as Onethread, to streamline project execution. Such software allows you to create plans, assign tasks, facilitate communication and collaboration among project members, and keep everyone informed about task progress.
By diligently navigating the project execution phase and addressing challenges proactively, project teams can work towards successfully delivering the desired outcomes.
Phase 4: Project Performance
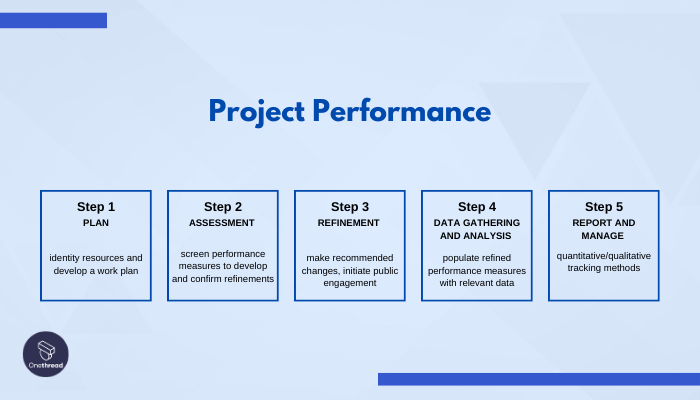
The project performance phase focuses on measuring the progress and overall performance of the project to ensure alignment with the project management plan. Various techniques are employed by project managers to assess performance. Some utilize project management software, while others rely on key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge whether the project is on track or not.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Project Performance
Several common KPIs are utilized to evaluate project performance:
- Project Objectives: Staying on schedule and within the desired budget indicates that the project is likely to meet the expectations of decision-makers and clients.
- Quality Deliverables: Assessing whether the project is meeting the standards and producing the desired deliverables is essential in determining overall performance.
- Cost Tracking: Project managers need to take accountability for the effort and cost of resources involved in the project.
- Project Performance: Any modifications made to the project due to scope creep or unforeseen circumstances are considered when measuring the overall progress of the project.
Tip: Review, Track, and Adjust
After completing each phase, it is important to conduct a thorough review, track the progress, and make any necessary adjustments to the project plan. This ensures that the project is delivered in the best possible manner, addressing any emerging challenges or changes in circumstances.
By actively monitoring project performance through appropriate measurement techniques and making necessary adaptations, project managers can ensure that the project stays on track and successfully meets its objectives.
Phase 5: Project Closure
The project closure phase signifies the completion of the project. It is the final stage of project management, also known as the post-mortem or follow-up phase. Effective project managers allocate dedicated time to assess the project’s strengths, recognize valuable team members, identify areas of improvement, rectify any issues, and derive key takeaways from the project.
While some project managers may consider this phase unnecessary, investing time in analyzing strengths and weaknesses can bring valuable insights for future projects, fostering enthusiasm and dedication.
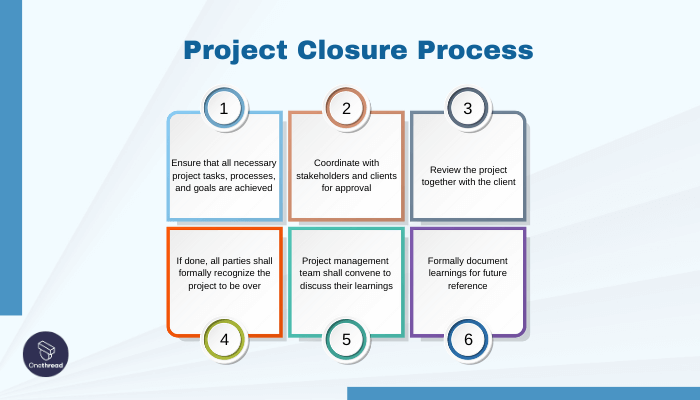
Steps for Project Closure
To close the project effectively, project managers undertake the following steps:
- Project Performance Evaluation: The project manager reviews performance reports to assess the project’s success and identify areas that went exceptionally well or did not go as planned. This evaluation helps in understanding the overall performance of the project.
- Conducting a Final Team Meeting: A final team meeting serves as a platform to reflect on the project’s achievements and share important insights and takeaways with team members. This enables the team to improve future project handling.
- Project Closure: Mission Accomplished: Upon completing the necessary assessments and team discussions, the project is officially closed, signifying its conclusion.
Tip: Utilizing Cloud-Based Software
Using a cloud-based software solution facilitates efficient management of project documents throughout the project’s lifecycle. This allows for seamless organization and storage of all relevant project information in one central location.
By actively closing a project with careful evaluation and open communication, project managers can leverage valuable insights for future projects, ensuring continuous improvement and success.
The Importance of Project Phases: Structuring and Streamlining Project Delivery
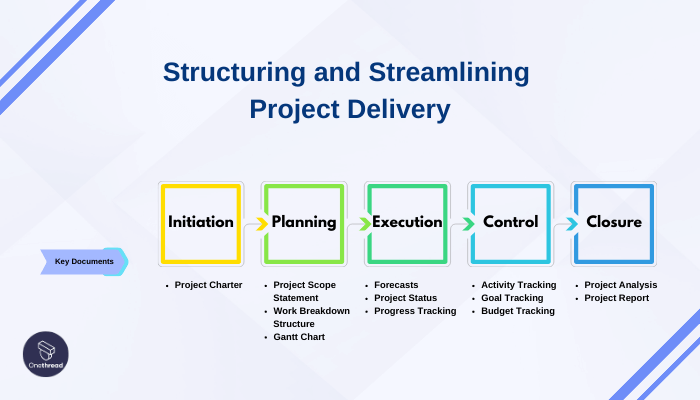
Project phases play a crucial role in managing and delivering successful projects. They provide a structured approach, ensure goal alignment, and facilitate effective resource allocation.
Managing Focus, Resources, and Alignment:
Dividing a project into phases helps manage the team’s focus and ensures alignment with clients and stakeholders.
By allocating resources according to each phase, teams can optimize their utilization and improve overall project efficiency.
Phases enable clear communication and understanding among team members and stakeholders, as defined roles and responsibilities are established.
Goal-Oriented Deliverables:
Thinking in terms of phases ensures that deliverables produced at the end of each phase align with the project’s goals.
Each phase acts as a milestone, providing an opportunity for evaluation and adjustment before progressing to the next phase.
Proper preparation during each phase enhances the team’s readiness for subsequent stages.
Structured Roadmap and Communication:
Project life cycle phases provide a clear and common roadmap for the project team to follow.
Defined activities, outputs, and responsibilities establish a visible framework that is easily understood by all stakeholders.
Assigning responsibilities by phase streamlines communication and clarifies the team’s focus during each stage.
Tracking Progress and Evolution:
Working on projects phase by phase enables accurate tracking of progress and linking it directly to each phase.
Completion of each phase becomes easily recognizable and celebrated by all involved.
The progressive evolution of the project allows for identification of areas needing attention and facilitates structured reviews to support project governance.
Project phases are essential for effective project management. They enable teams to manage focus, allocate resources efficiently, and align the project’s entire life cycle with clients and stakeholders.
By providing a structured roadmap, clarifying responsibilities, and facilitating progress tracking, project phases contribute to successful project delivery. While adhering to industry standards like PMBOK is recommended, project teams have flexibility in adopting their own system based on industry-specific factors and organizational policies.
Conclusion
The project life cycle is an essential tool in project management, providing a structured approach to guide projects from start to finish. The project life cycle 5 phases, namely initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure, offer a systematic framework that helps project managers and teams navigate through various stages of a project.
By understanding and effectively utilizing these phases, organizations can enhance project outcomes, mitigate risks, and optimize resource utilization. Remember, the project life cycle is a dynamic process, and adapting it to suit the unique needs of each project is crucial for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Initiation Phase Of The Project Life Cycle?
The initiation phase is the starting point of a project, where the project’s feasibility and alignment with organizational objectives are assessed. It involves defining the project scope, identifying stakeholders, and conducting a preliminary analysis to determine if the project is worth pursuing.
What Happens During The Planning Phase Of The Project Life Cycle?
The planning phase focuses on defining project goals, developing a comprehensive project plan, and creating a roadmap for project execution. This phase involves tasks such as resource allocation, scheduling, risk assessment, and creating a communication plan.
What Is The Execution Phase In The Project Life Cycle?
The execution phase is where the actual work of the project takes place. The project plan developed during the planning phase is put into action, and the project team works towards achieving the project objectives. This phase involves task implementation, team coordination, and regular progress monitoring.
What Is The Significance Of The Monitoring And Control Phase In The Project Life Cycle?
The monitoring and control phase is crucial for tracking the progress of the project and ensuring that it stays on track. Project managers and teams use performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the project’s progress, identify any deviations from the plan, and take corrective actions to keep the project on schedule and within budget.
What Activities Are Involved In The Closure Phase Of The Project Life Cycle?
The closure phase marks the formal end of a project. It involves finalizing and documenting project deliverables, conducting project evaluations, and celebrating the project’s completion. This phase also includes lessons learned sessions to capture valuable insights that can be applied to future projects.