In today’s fast-paced professional landscape, mastering project management tools and techniques are essential for boosting overall performance. Furthermore, to improve productivity, simplify the workflow, and happiness levels at work.
Elevate your performance, and discover the transformative impact with the right tools and techniques. These invaluable resources empower you to efficiently navigate complex projects, streamline processes, and achieve desired outcomes.
From collaborative software solutions to proven methodologies, project management offers many tools and techniques to optimize your workflow.
By incorporating them seamlessly into your daily routine, you can embark on a path to success and satisfaction in your professional endeavors.
Importance of Project Management Tools and Techniques
Project management techniques are crucial for success. They provide structure and clarity. Risks are identified and managed. Deadlines are met, keeping projects on schedule. Quality is maintained.
Overall, project management techniques ensure efficient and successful project completion. Let’s have a look at some of it:
- It helps streamline various aspects of project planning, execution, and monitoring, ensuring efficient workflows.
- It provides centralized platforms to organize project documentation, tasks, timelines, and resources, ensuring clarity and easy access to information.
- By automating repetitive tasks, project management tools save time and effort, allowing teams to focus on value-added activities and meet project deadlines.
- Tools provide real-time insights and data visualization, empowering project managers to make informed decisions and adjustments based on accurate information.
- Establish clear responsibilities and accountability among team members, ensuring everyone is aligned and focused on achieving project goals.
- With tools for status updates, progress tracking, and reporting, project managers can effectively communicate project status and progress to stakeholders, building trust and maintaining transparency.
Top Project Management Tools
Here are three project management tools highly regarded for their capabilities, versatility, and popularity among teams in various industries.
1. Onethread:

Onethread is a project management tool that offers a comprehensive platform for planning, executing, and tracking projects. With its user-friendly interface and robust features, Onethread helps teams streamline their project workflows and enhance collaboration.
Here are some key features of Onethread:
- Task Management: Create, assign, and track tasks with ease. Stay organized and ensure everyone knows their responsibilities.
- Project Planning: Plan projects effectively by setting goals, defining project scope, and establishing timelines and milestones.
- Communication and Collaboration: Collaborate seamlessly with team members through integrated messaging, file sharing, and commenting features.
- Document Management: Keep project-related documents organized and easily accessible in one centralized location.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor project progress in real-time and get a clear overview of task completion and milestones achieved.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate insightful reports and analytics to gain valuable project insights, track performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Onethread simplifies project management by providing a comprehensive set of features and tools that empower teams to collaborate effectively, track progress, and achieve project success.
2. Asana:
Asana’s intuitive and visually appealing interface makes navigating and understanding the tool’s features easy for users. This user-friendly design promotes adoption and seamless integration into workflows. Some key features of Asana,
- Flexible Task Views: Asana offers versatile task views (List, Board, Calendar) for flexible project management, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- Automation Features: Asana automates tasks with custom “Rules” to automate repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing manual effort.
- Project Templates: Asana offers templates tailored to specific project types, such as marketing campaigns, product launches, or event planning, accelerating project initiation to ensure quick setup and streamlined workflows.
- Portfolio Management: Asana excels in portfolio management, providing a holistic view of multiple projects for efficient decision-making and resource optimization.
- Custom Fields and Workflows: Asana offers customizable fields and workflows, empowering teams to tailor the tool to their specific project needs for improved organization and consistency.
These unique features and capabilities make Asana a versatile and comprehensive project management tool that caters to the diverse needs of teams, enabling them to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and achieve project success.
3. Trello:
Trello, a popular project management tool, offers several key features,
- Boards, Lists, and Cards: Trello’s organizational structure revolves around boards, lists, and cards for efficient task management and organization.
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: Trello’s drag-and-drop interface simplifies task management and updates by allowing users to easily move cards across lists or boards.
- Labels and Labels-Based Filtering: Trello enables users to add tags to cards for easy categorization and visual differentiation of tasks based on criteria like priority, type, or responsible team member. Filtering cards based on labels allows for quick access and organization.
- Due Dates and Reminders: Users can set dates and reminders on Trello cards to ensure the timely completion of tasks. The platform also provides notifications and email reminders for updates and approaching deadlines.
- Comments and Activity Tracking: Users can leave comments on Trello cards for efficient communication and collaboration. The platform also maintains a detailed activity log, capturing all card changes, comments, and updates for a comprehensive project history.
- Power-Ups and Integrations: Trello offers various power-ups and integrations with tools like Slack, Google Drive, Jira, and more, expanding its functionality and enabling seamless workflow integration.
These key features make Trello a flexible and versatile project management tool, enabling users to visually organize tasks, collaborate seamlessly, and efficiently manage their projects.
Effective Project Management Techniques
1. The waterfall methodology
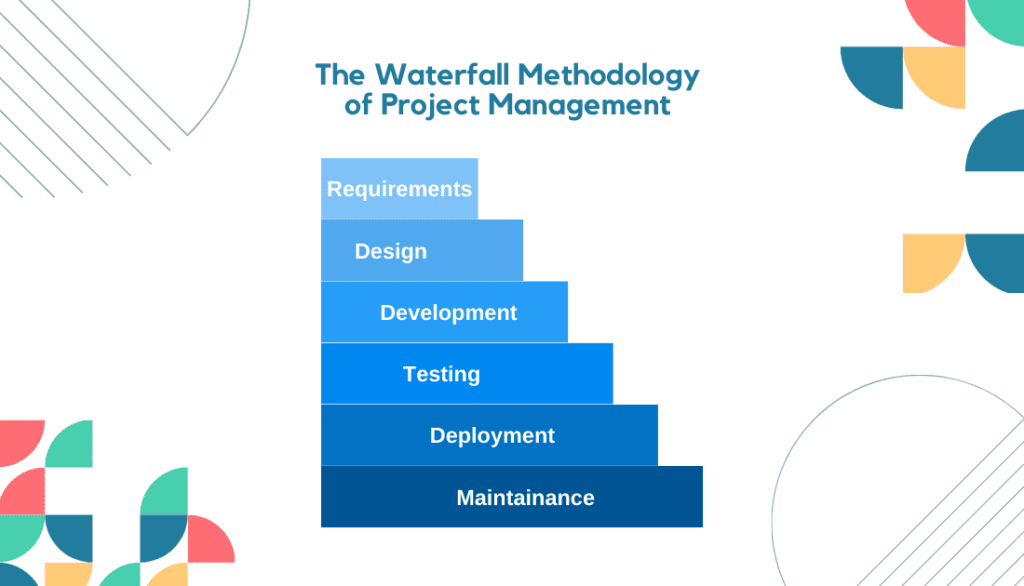
It is a sequential project management approach that follows a linear and structured progression from one project phase to another. It comprises distinct stages: requirements gathering, design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance.
Here are the key characteristics of the waterfall methodology:
- Linear Flow: The waterfall methodology follows a step-by-step progression, with each phase dependent on the completion of the previous one.
- Emphasis on Documentation: Documentation is crucial in the waterfall approach, with detailed requirements and specifications documented upfront.
- Clear Milestones: The methodology sets milestones and deliverables for each phase, providing a structured timeline for project completion.
- Flexibility: The waterfall methodology needs to be more flexible, as changes made during later stages can be costly and time-consuming.
- Suitable for Stable Requirements: It is best suited for projects with well-defined and stable requirements, where the end goal is clear from the beginning.
Overall, the waterfall methodology offers a systematic and planned approach to project management, ensuring a clear project path and minimizing the risk of scope creep.
2. Agile methodology
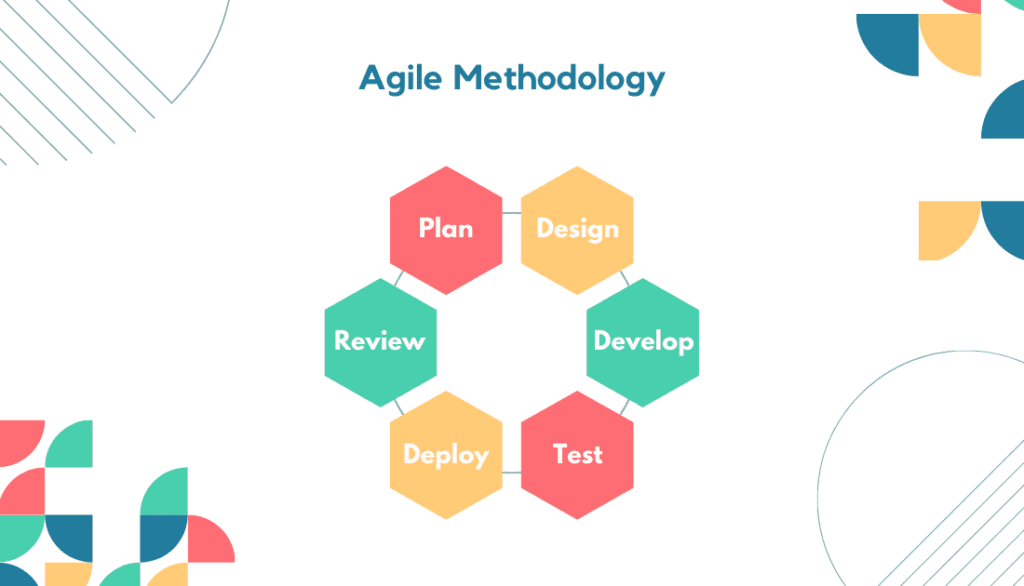
It is a flexible and iterative project management approach that delivers value through continuous collaboration and adaptation. It emphasizes adaptive planning, cross-functional teams, and iterative development cycles known as sprints.
The pros of Agile methodology include the following:
- Flexibility: Agile allows for changes and adaptations to project requirements throughout development.
- Collaboration: It promotes close cooperation between team members, stakeholders, and customers, fostering better communication and shared understanding.
- Faster Feedback: Frequent iterations and feedback loops enable quicker identification and resolution of issues or changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Agile’s focus on delivering incremental value ensures customer satisfaction by providing an early and continuous product or project delivery.
However, there are some cons to consider:
- Scope Creep: The flexibility of Agile can sometimes lead to scope creep if not managed effectively, resulting in project delays or increased costs.
- Documentation: Agile emphasizes working software over comprehensive documentation, which may be challenging for organizations requiring extensive documentation for compliance or regulatory purposes.
- Learning Curve: Adopting Agile may require a mindset shift and learning new practices, which can initially slow down the team’s productivity.
Despite its challenges, Agile methodology offers many benefits, allowing teams to respond to changing requirements, deliver value iteratively, and foster a collaborative and customer-centric approach to project management.
3. Critical Chain Methodology (CCM)
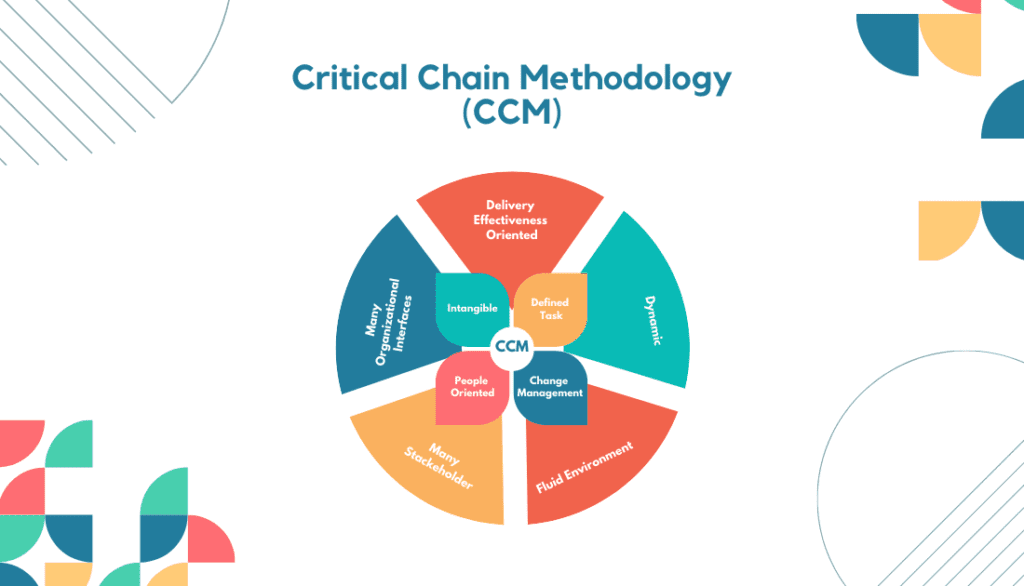
The Critical Chain Methodology is a project management technique that focuses on optimizing the use of resources and schedules to complete projects efficiently. It addresses the issues of traditional project management methods that often suffer from poor scheduling and resource allocation.
CCM emphasizes the identification of project dependencies and critical paths, allowing for a more accurate estimation of project duration and resource requirements.
Pros:
- Efficient resource allocation and optimization.
- Improved project completion time.
- Increased focus on project dependencies and critical paths.
- Clear identification of project constraints and risks.
Cons:
- Complex implementation and understanding.
- Requires proper training and expertise.
4. Critical Path Methodology (CPM)
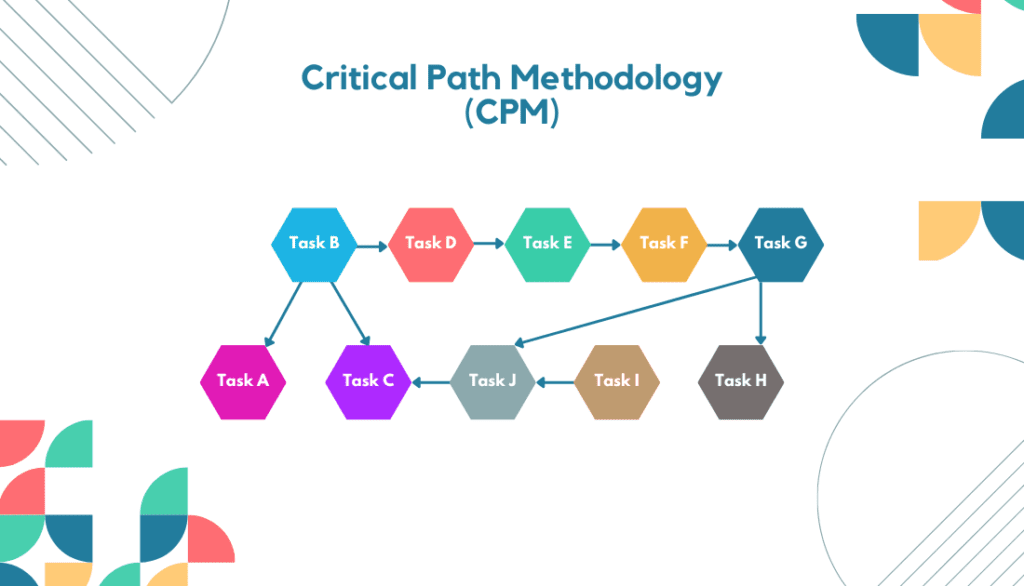
The Critical Path Methodology is a project management technique that schedules and manages complex projects. It involves identifying the critical path, the longest sequence of dependent tasks determining the project’s overall duration.
CPM helps project managers prioritize activities and allocate resources effectively by analyzing task dependencies and estimating task durations.
Pros:
- Efficient project scheduling and resource management.
- Clear identification of critical tasks and their impact on project duration.
- Effective tool for managing complex projects with numerous dependencies.
- Provides a visual representation of project timelines and dependencies.
Cons:
- Limited flexibility for accommodating changes or delays.
- Requires accurate estimation of task durations.
- Relies heavily on task dependencies, which can be complex to analyze.
5. Scrum Methodology
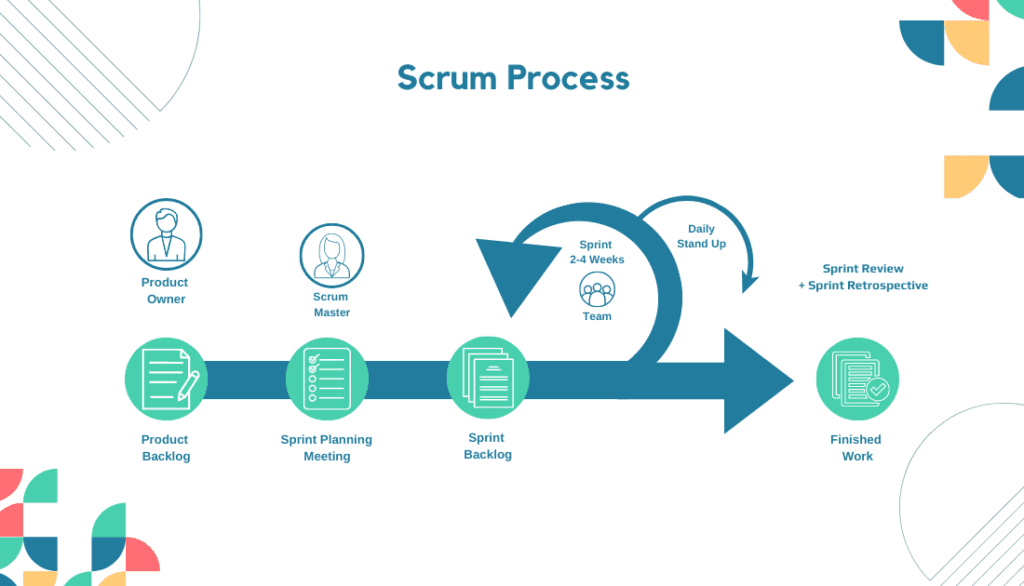
Scrum Methodology is an agile project management technique that promotes collaboration, adaptability, and iterative development. It focuses on delivering value in short iterations called sprints.
Scrum utilizes a cross-functional team approach with clearly defined roles, including a product owner, scrum master, and development team. This methodology’s key components are daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, and sprint reviews.
Pros:
- Enhanced collaboration and communication within the team.
- Increased adaptability to changing project requirements.
- Frequent product delivery and customer feedback.
- Transparency and visibility into project progress.
Cons:
- It may not be suitable for projects with fixed scopes or requirements.
- Requires a dedicated scrum master and adherence to scrum ceremonies.
- Limited scalability for large and complex projects.
6. Kanban Methodology

Kanban Methodology is a project management technique that visualizes work, limits work in progress (WIP), and improves flow. It utilizes a Kanban board to visualize tasks and their status, typically represented by columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.”
Kanban emphasizes managing WIP to avoid bottlenecks and maintain a smooth workflow.
Pros:
- Clear visualization of work progress and bottlenecks.
- Flexibility to accommodate changing priorities and requirements.
- Improved flow and efficiency in task completion.
- Encourages collaboration and promotes team autonomy.
Cons:
- Less suitable for complex projects with intricate dependencies.
- Requires constant monitoring and updating of the Kanban board.
- It may need to provide a detailed timeline or long-term planning perspective.
7. Event Chain Methodology
Event Chain Methodology is a project management technique focusing on managing and mitigating risks associated with project activities and events. It recognizes that uncertainties and risks can significantly impact project outcomes.
Event Chain Methodology identifies and analyzes potential events and their interdependencies to develop effective risk response strategies.
Pros:
- Proactive identification and management of project risks.
- Improved risk mitigation and contingency planning.
- Provides a structured approach for incorporating risk management into project planning.
- Enhances overall project resilience and adaptability.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to identify and analyze event chains.
- Complexity in accurately estimating event probabilities and impacts.
- It may overlook certain risks or dependencies if not carefully considered.
8. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
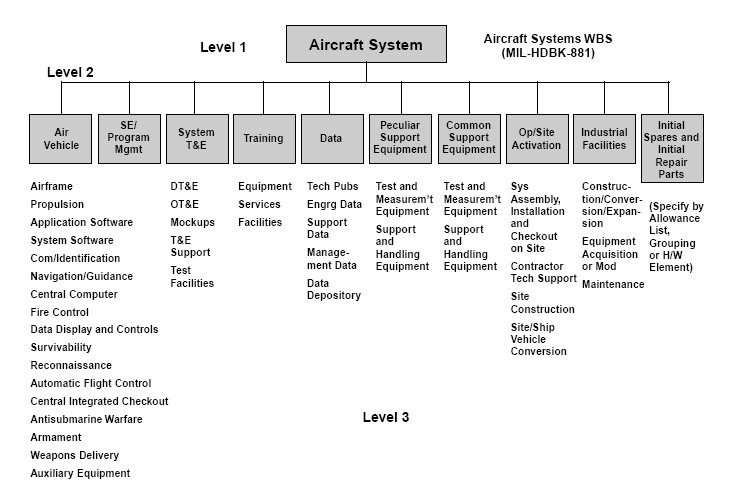
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a project management technique that breaks down a project into smaller, manageable components or work packages. It provides a hierarchical representation of project deliverables, tasks, and sub-tasks, helping to organize and structure project activities.
Pros:
- Provides a clear and visual representation of project scope and structure.
- Facilitates effective project planning, resource allocation, and scheduling.
- Enhances communication and coordination among project team members.
- Enables accurate estimation of project duration and costs.
Cons:
- Requires careful planning and coordination to develop a comprehensive WBS.
- It can become complex and time-consuming for large and complex projects.
- Difficulties may arise in assigning ownership and responsibility for each work package.
9. Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
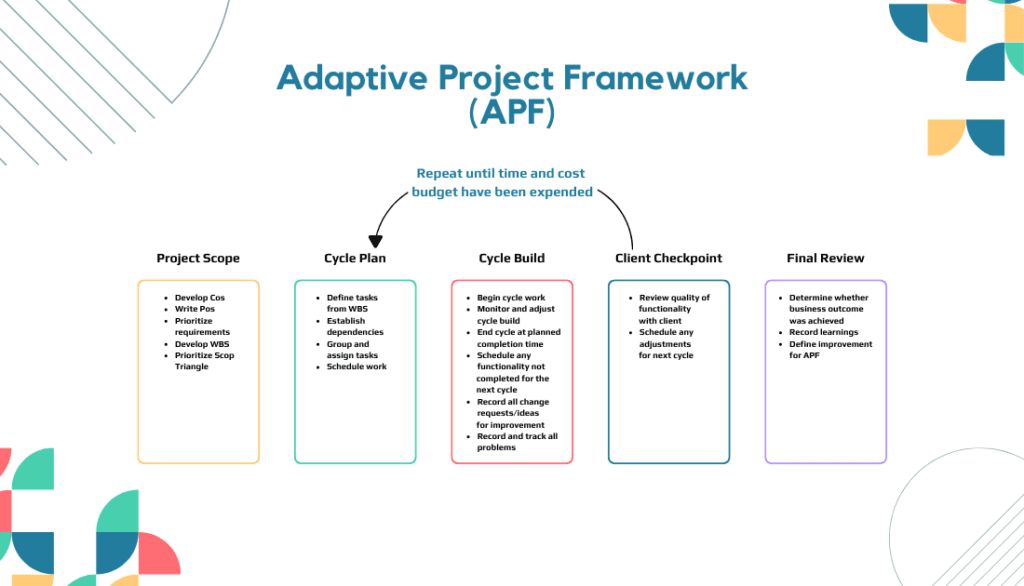
The Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is a project management technique that emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and continuous learning. It recognizes that project requirements and goals may evolve, and encourages a collaborative approach to effectively accommodate changes. APF focuses on iterative development and feedback loops to enhance project outcomes.
Pros:
- Allows for flexibility in responding to changing project requirements.
- Encourages collaboration and continuous learning throughout the project lifecycle.
- Facilitates early and frequent stakeholder involvement and feedback.
- Adapts well to projects with uncertain or evolving requirements.
Cons:
- Requires active and ongoing communication among project stakeholders.
- It may be challenging to implement in environments with rigid project management structures.
10. Extreme Project Management (XPM)
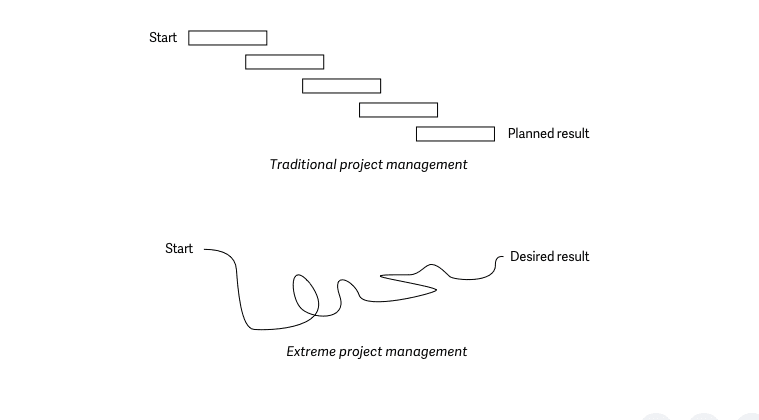
Extreme Project Management (XPM) is a project management technique focusing on adaptability and flexibility in rapidly changing environments. It is beneficial for projects that involve high uncertainty and innovation.
XPM emphasizes collaboration, iteration, and close customer involvement throughout the project lifecycle.
Pros:
- One of the major advantages of XPM is its ability to respond quickly to changes, enabling teams to adjust plans and requirements as needed.
- It promotes transparency, team empowerment, and faster decision-making.
Cons:
- Potential difficulty in maintaining stability and predictability,
- Increased risk of scope creep and challenges in managing expectations and dependencies.
- Careful planning and skilled leadership are crucial for successfully implementing XPM.
11. Extreme Programming
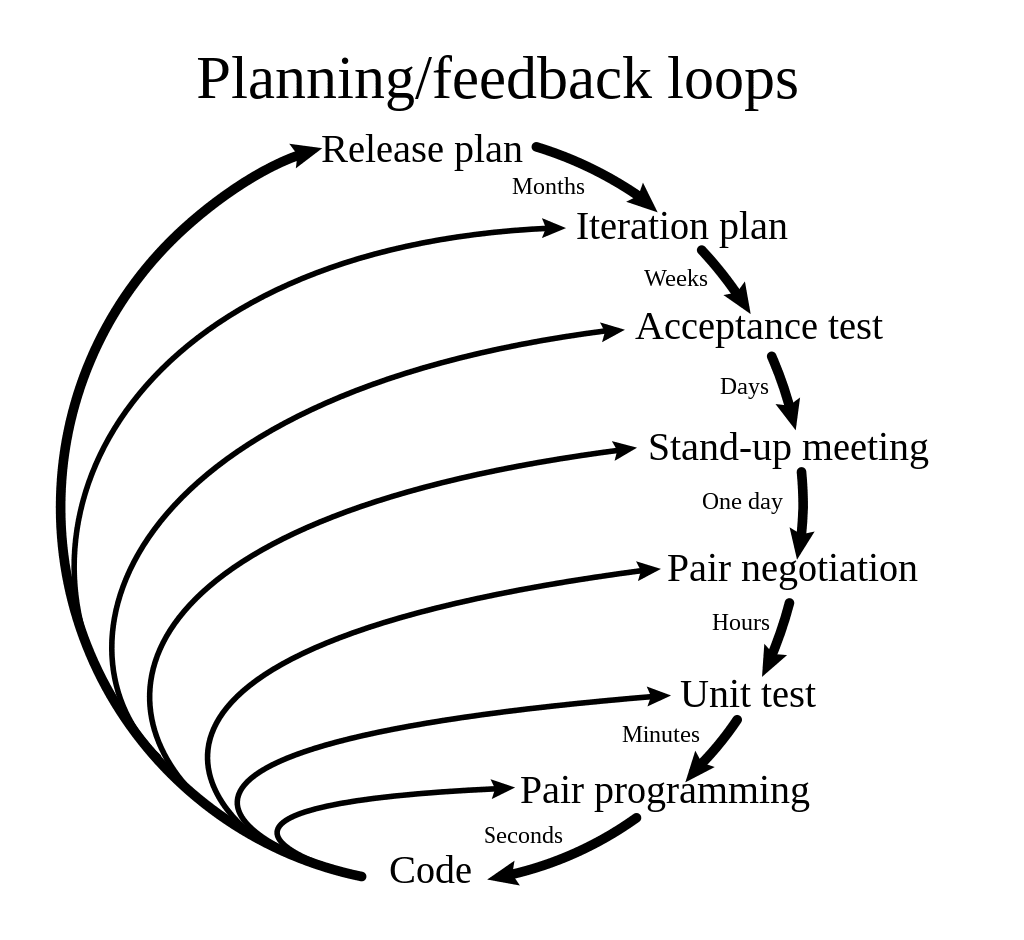
Extreme Programming (XP) is an agile project management technique emphasizing collaboration, adaptability, and iterative development. It promotes frequent communication, simplicity, and quick feedback loops to deliver high-quality software.
XP employs several practices, including test-driven development, continuous integration, pair programming, and short development iterations.
Pros:
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through continuous involvement and frequent releases.
- Improved software quality due to rigorous testing and constant refactoring.
- Increased productivity with efficient collaboration and shared ownership.
- Quick adaptation to changing requirements and reduce project risks.
- Greater transparency and visibility through open communication and regular demos.
Cons:
- Requires a highly motivated and experienced team to implement all practices effectively.
- Limited documentation may lead to knowledge gaps and challenges in maintaining the codebase.
- Strict adherence to XP practices may reduce flexibility for certain project types.
12. Process-Based Project Management
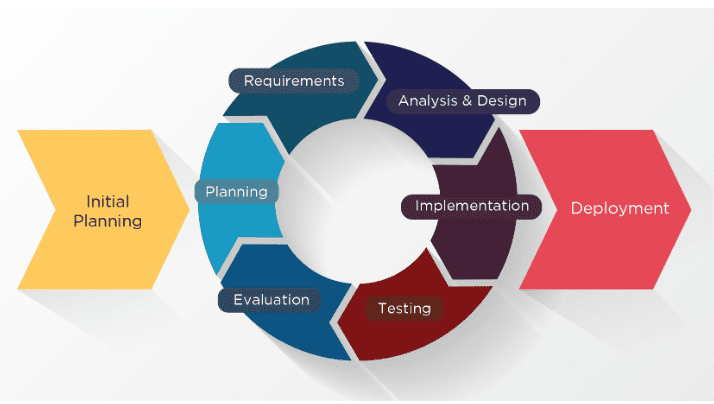
Process-Based Project Management is a technique that defines and follows a structured set of processes and procedures throughout the project lifecycle. It emphasizes standardization, consistency, and adherence to predefined methods and guidelines. This approach ensures a systematic and predictable workflow.
Pros:
- Provides a standardized approach to project execution, ensuring consistency and predictability across projects.
- By defining and following established processes, project teams can streamline workflows, reduce duplication of effort, and improve overall project efficiency.
- Allows for scalability, making it easier to replicate successful processes and adapt them to different projects and teams.
Cons:
- Strict adherence to predefined processes may limit the ability to adapt and respond to unique project circumstances or changing requirements.
- It may stifle creativity and innovative thinking, focusing more on following established procedures rather than exploring new approaches.
- Often requires extensive documentation, which can be time-consuming and may divert resources from actual project execution.
13. Rational Unified Process (RUP)
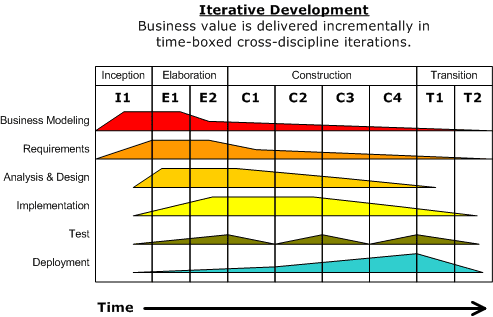
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a project management technique that offers a disciplined approach to software development. It employs an iterative and incremental framework emphasizing collaboration, risk management, and development cycles.
RUP incorporates best practices, templates, and guidelines for each development lifecycle phase.
Pros:
- Improved project visibility.
- Effective risk management.
- Focus on quality.
- Promotes collaboration.
Cons:
- Complexity and resource requirements.
- Challenges in tailoring to specific project needs.
- Time-consuming documentation processes.
14. PMBOK Method
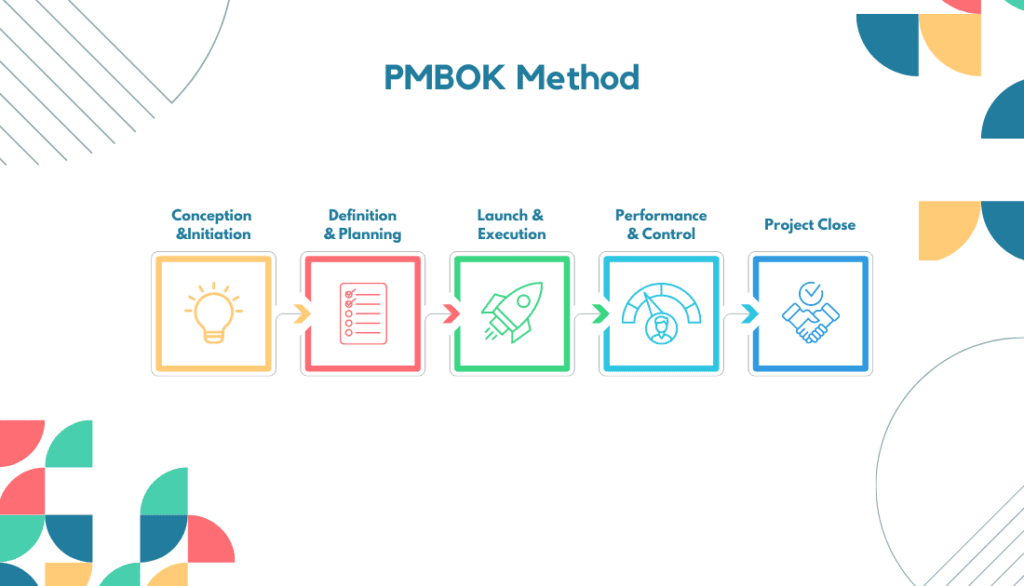
The PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) Method is a widely recognized project management technique that provides a comprehensive framework for managing projects. It encompasses best practices, processes, and knowledge areas to guide project managers.
Pros:
- Versatility across industries and project types.
- A standardized approach for consistency.
- Emphasis on risk management.
- A common language for project teams.
Cons:
- Extensive documentation requirements.
- Potential rigidity in certain situations.
- Customization is needed for specific project needs.
15. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a project management technique that helps plan, schedule, and control complex projects. PERT utilizes a network diagram to represent project tasks and their dependencies.
It estimates the duration of each task using three-time estimates: optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely. This approach allows for better project planning and risk assessment.
Pros:
- Improved scheduling accuracy.
- Effective resource allocation.
- Better visibility into critical project paths.
Cons:
- Overemphasis on time estimates.
- Difficulty in handling uncertainties.
- Complexity in setting up and maintaining the network diagram.
16. Project in Controlled Environment (Prince2)
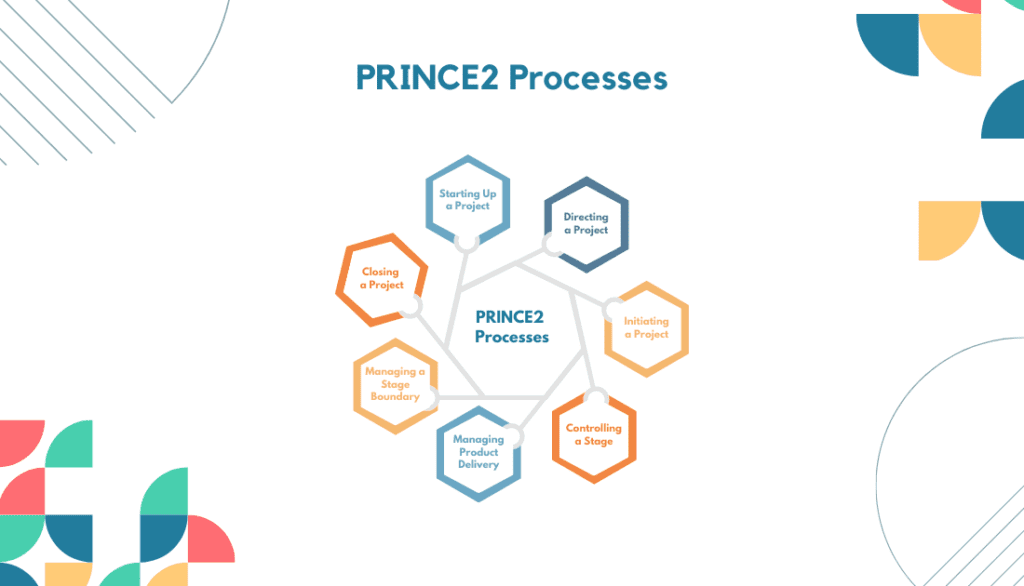
PRINCE2 (Projects in Controlled Environments) is a project management technique widely used in various industries. It offers a structured and process-based approach to managing projects. PRINCE2 focuses on clear project roles and responsibilities, defined stages, and thorough project documentation.
Pros:
- Improved project control.
- Effective risk management.
- Better stakeholder communication.
Cons:
- Rigid and requires customization for certain projects.
- Significant administrative overhead.
- Not suitable for small or simple projects.
Conclusion
Incorporating these tools and techniques into your workflow can revolutionize your project management experience. These tools empower you to achieve greater productivity, optimize project timelines, and mitigate risks.
Embracing the tools and techniques not only improves your overall performance and contributes to a happier and more fulfilling work environment.
Take advantage of these tools and watch your projects thrive.
FAQs
How do project management tools simplify projects?
Project management tools simplify projects by streamlining processes, enhancing collaboration, optimizing resource allocation, and providing clear visibility into project progress and timelines.
Which project management tools are suitable for small businesses?
Popular project management tools suitable for small businesses include Onethread, Trello, and Asana.
Are there any free project management tools available?
Yes, there are free project management tools available. But with limited features and with some restrictions on the free plan.
Can project management tools be customized for specific industries?
Yes, project management tools can be customized to cater to specific needs and requirements.
